Fig. 1.
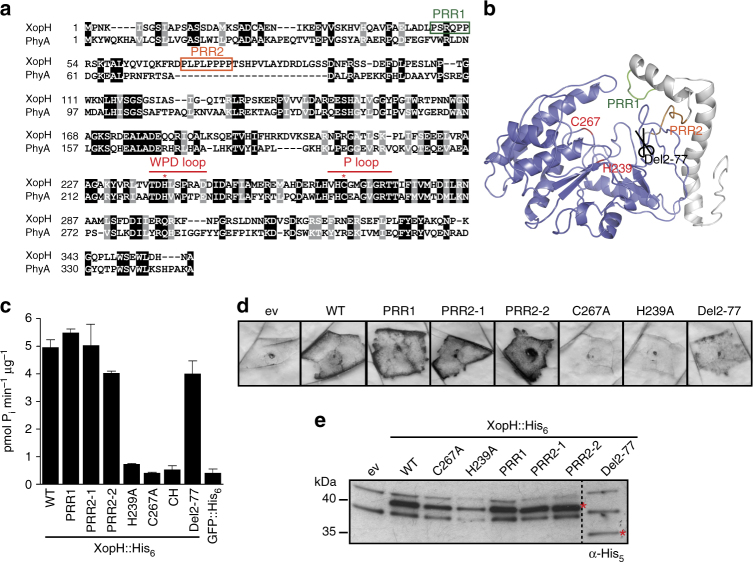
XopH possesses phytate-degrading activity that is required for HR induction. a Amino acid (aa) sequence alignment of XopH with the Selenomonas ruminantium phytase generated with T-Coffee66. Identical and similar aa are shaded black and gray, respectively, using Boxshade67. Dashes indicate gaps. Catalytic residues in the WPD and P loops are marked by asterisks. Proline-rich regions (PRRs) are boxed. b XopH protein structure modeled after the S. ruminantium phytase crystal structure (pdb 1U24) using Phyre214, visualized by PyMol68. Blue, phytase domain; gray, N-terminal domain (aa 1–77). c InsP6 dephosphorylation by XopH (WT) and mutants, respectively. PRR1, P48,52,53A; PRR2-1, P69,71A; PRR2-2, P73,74,75,76A; CH, H239A/C267A; Del2-77, deletion of aa 2–77. GFP served as negative control. Values are means of two technical replicates. Error bars indicate s.d. The experiment was performed twice with similar results, using two independent protein preparations each. d HR induction in pepper ECW-70R (Bs7) leaves after Agrobacterium-mediated expression of XopH and mutant variants. Two days post inoculation (dpi), leaves were bleached in ethanol for better visualization of the HR. e Protein expression, two dpi, in the same plants analyzed in d. Immunoblot signals at expected sizes are marked by asterisks. The experiment was repeated twice with similar results