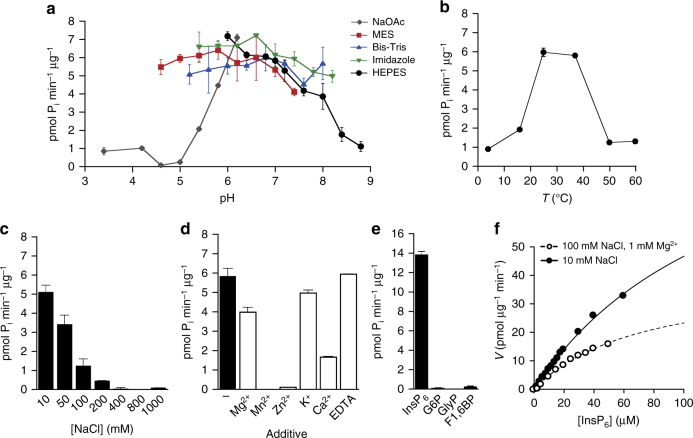
Fig. 2.
Characterization of the XopH phytase activity. a XopH activity in presence of 10 mM NaCl in different buffering systems. b XopH activity in presence of 100 mM NaCl and 1 mM MgCl2 at different temperatures (16, 25, 37, 50, and 60 °C). c XopH activity in buffer with 10–1000 mM NaCl. d XopH activity in absence and presence of 1 mM metal ions or 1 mM EDTA. Reaction buffer contained 10 mM NaCl. e XopH-dependent dephosphorylation of 0.1 mM InsP6, glucose-6-phosphate (G6P), glycerol phosphate (GlyP), and fructose 1,6-bisphosphate (F1,6BP), respectively. f Kinetics of InsP6 dephosphorylation by XopH. Data were fitted to Michaelis Menten equation using KaleidaGraph4.0 (www.synergy.com). V max and K M in presence of 100 mM NaCl and 1 mM MgCl2 (open circles) are 40.0 ± 5.1 pmol µg−1 min−1 and 72.9 ± 13.7 µM, and in presence of 10 mM NaCl (closed circles) 110.6 ± 9.5 pmol µg−1 min−1 and 138.3 ± 15.0 µM. Values are means of two technical replicates. Error bars indicate s.d. The experiments were performed twice with similar results, using two independent protein preparations each