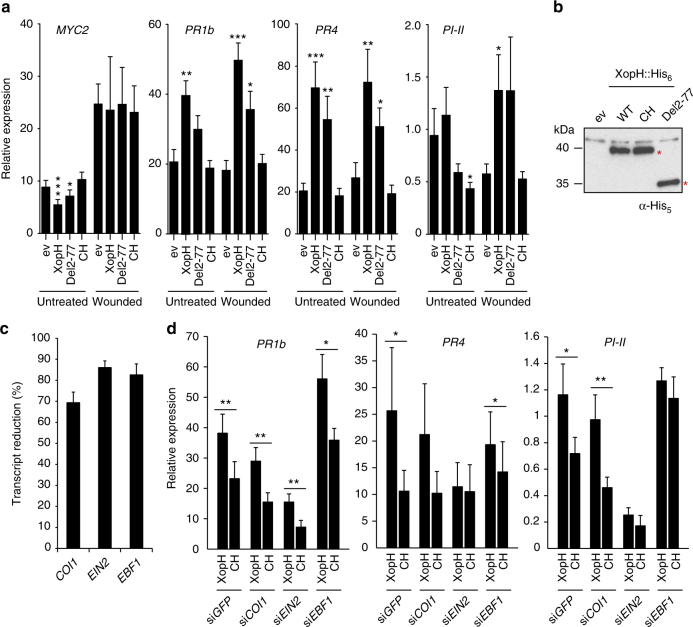
Fig. 8.
XopH phytase activity affects plant hormone pathways. a qRT-PCR analysis of N. benthamiana leaves transiently expressing XopH and mutant derivatives, untreated or 20 min post wounding. ev empty T-DNA. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences to corresponding ev samples (Mann–Whitney test; *p < 0,05; **p < 0,01; ***p < 0,001). b Protein expression two dpi in the same plants analyzed in a. Immunoblot signals at expected sizes are marked by asterisks. c qRT-PCR analysis of COI1-, EIN2-, and EBF1-silenced N. benthamiana plants (siCOI1, siEIN2, and siEBF1) transiently expressing XopH and its catalytically inactive variant (CH), respectively. GFP-silenced plants (siGFP) served as control. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences (Student’s t test; *p < 0,05; **p < 0,01). d Silencing efficiencies determined by qRT-PCR. Values indicate percent reduction of COI1, EIN2, and EBF1 transcript levels in the respective silenced plants, relative to GFP-silenced plants, both expressing inactive XopHCH. Combined data from three independent experiments (with three biological replicates per experiment) are shown (a, c, d). Error bars indicate s.e.m.