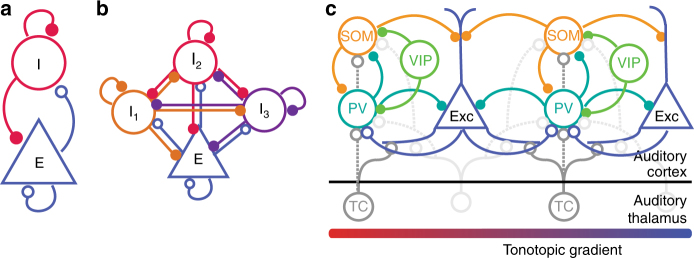
Fig. 1.
Simplified views of cortical circuits. (a) Diagram of excitatory–inhibitory circuit with recurrent connections. Theoretical and experimental studies demonstrate that inhibition stabilizes between excitatory and inhibitory neurons in the auditory cortex. (b) Inhibitory–excitatory network can be extended to include several interneuron subtypes. (c) Schematic diagram of connectivity between select neurons in the auditory cortex (note that layer-specific information is omitted here): Exc: Excitatory neurons; PV: parvalbumin-positive interneurons; SOM: somatostatin-positive interneurons; VIP: vasopressin-positive interneurons; TC: Thalamo-cortical projection neurons. All neuron types receive additional inputs from other brain areas, which were omitted from the diagram for simplicity. Open circles: excitatory synapses; closed circles: inhibitory synapses. Solid lines indicate dominant projections; dashed lines indicate occasional connections