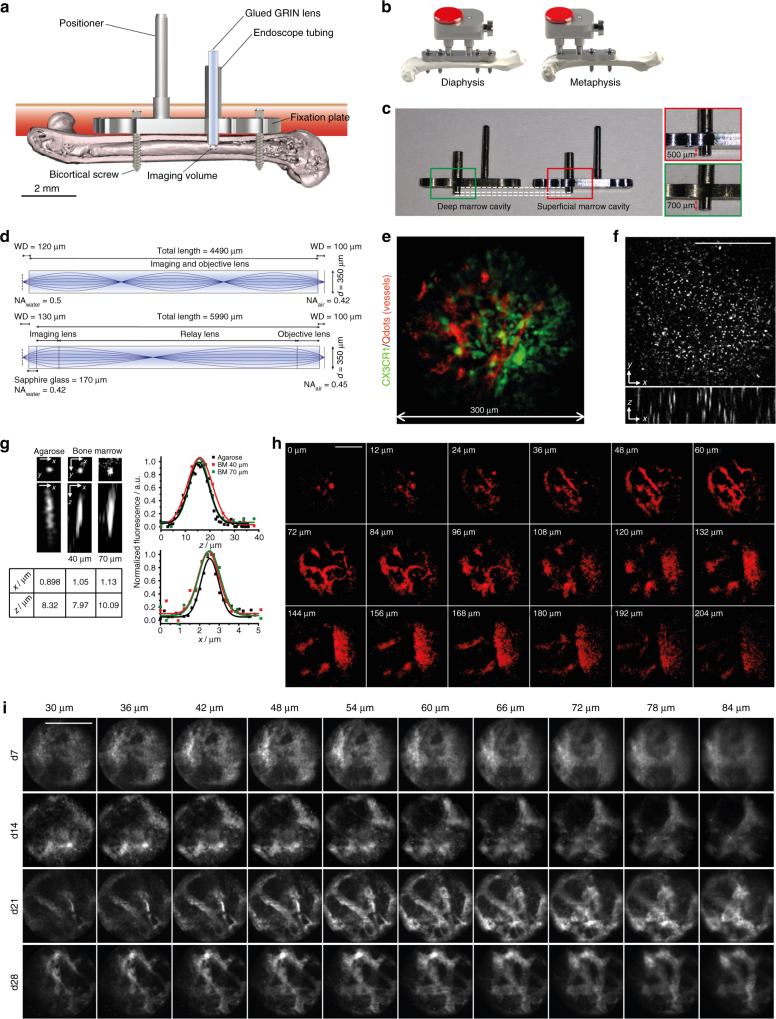
Fig. 1.
LIMB allows murine long bone imaging in various locations with high resolution. a Design and positioning of LIMB implant for longitudinal bone marrow imaging. The LIMB implant is fixed onto the femur using bi-cortical angle-stable screws. GRIN lens systems are placed within the endoscope tubing for imaging and sealed to ensure sterility. The positioner allows adjustment and alignment of GRIN and microscope optical axes. b In order to account for tissue heterogeneity, i.e., metaphyseal vs. diaphyseal regions, alternative LIMB designs have been developed. LIMB fixation with four screws allows higher bone stability after osteotomies. c Tubing lengths of 500 and 700 µm, respectively, allow access to either peri-cortical or deep marrow regions. d Two GRIN lens systems are used for imaging. The single GRIN lens (upper panel) combines the imaging and objective lens function and is glued into the endoscope tubing. The symmetric triple GRIN lens (lower panel) is exchangeable and a sapphire window seals the endoscope tubing. e 3D fluorescence image of the bone marrow of a CX 3 CR1:GFP mouse using the single GRIN lens (myeloid CX 3 CR1 + cells ‑ green; vasculature labeled by Qdots ‑ red). The maximum field of view is circular, with 280 µm diameter. f The PSF was measured on 100 nm beads (λ em = 605 nm, λ exc = 850 nm) in agarose, using the single GRIN lens. No significant wave-front distortions affecting the PSF are observed. g Qdots are used to estimate PSF in marrow tissue. They reveal slight resolution deterioration with increasing imaging depth. h 2D fluorescence images of Qdots-labeled femoral vasculature, 35 days post-surgery, at various z-positions between the surface of the single GRIN lens and 204 µm tissue depth. They reveal fine vascularization in the upper layers and a large blood vessel (~100 µm diameter) with emerging branches in the deep marrow. i 2D fluorescence images of femoral vasculature acquired at various depths and time points post-surgery, using the triplet GRIN lens. The tissue at the contact surface with the window is characterized by de novo micro-vascularization, i.e., granulation tissue. Its thickness varies between individuals and decreases over time after implantation. Scale bars = 100 µm