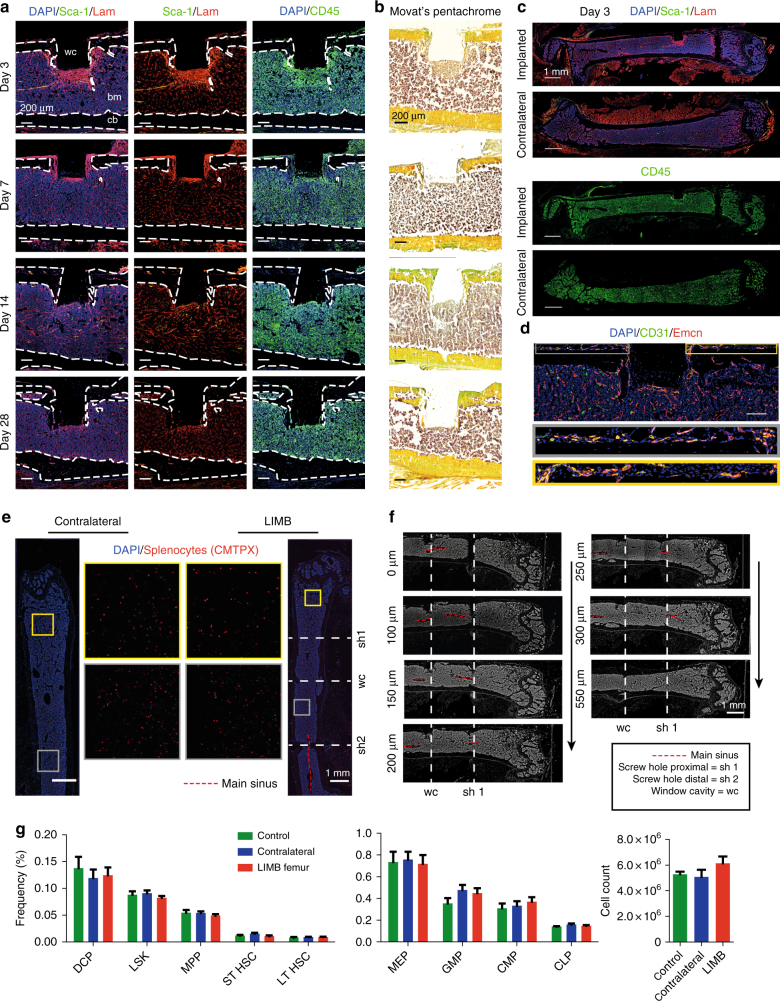
Fig. 3.
The bone marrow within the imaging volume reaches steady-state comparable to homeostasis 28 days after LIMB implantation. a Immunofluorescence analysis of bone sections after removal of the LIMB implant over the time course of 4 weeks. ECM formation was identified by the marker Laminin (Lam). Stem-cell antigen 1 (Sca-1) is highly expressed in arterioles. The leukocyte marker CD45 indicates localization of inflammatory cells adjacent to the window cavity (wc). Lam is highly expressed around the implant during the first week and completely normalizes after 2–4 weeks. CD45+ cell accumulations are found during the first weeks in proximity to the wc. b Movat’s pentachrome stain detects connective tissues and reveals remodeling of bone primarily on the periosteal interface near the fixation plate. a, b Images are representative for 3–5 mice per time point post-surgery. c Overview immunofluorescence images of the femoral bones from an individual mouse 3 days post-surgery. Note the specific reaction to the implant-bone marrow interfaces indicated by accumulations of CD45+ cells, and Lam+ and Sca1+ arteries (yellow). bm bone marrow, cb cortical bone. d Immunofluorescence image of the region around the endoscope tubing in a LIMB-implanted femur 7 days post-surgery, including the bone cortex and periosteum under the plate. The presence of various blood vessel subsets indicated by CD31 and Emcn demonstrates intact blood supply to the periosteum and to the bone. Scale bar = 100 µm. e Blood supply is intact throughout the marrow cavity, indicated by CMTPX-labeled splenocytes, which localize in the bone marrow 4 h after transplantation in both contralateral and LIMB-implanted femurs at 42 days post-surgery (n = 3 mice). f Histological DAPI stain (gray) shows intact tissue structure, with no separation of the bone marrow and the vasculature by the screws or endoscope tubing. g Flow cytometry analysis of femurs with the LIMB implant, their contralateral femurs and femurs of control mice. Similar frequencies and cell counts of various cell populations shows no effect of the LIMB implant on bone marrow cell composition (n = 8 LIMB-implanted mice, n = 8 controls, two independent experiments). Error bars represent s.e.m. values. Statistical analysis was performed using t-test