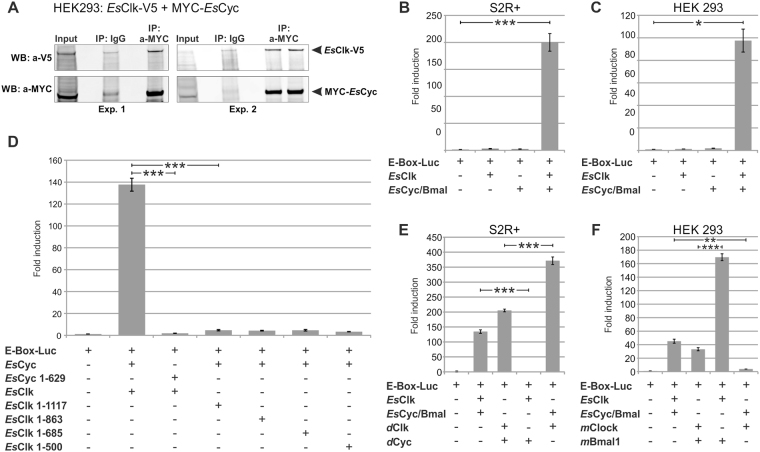
Figure 4.
EsCLOCK and EsCYCLE/BMAL dimerize and activate transcription from the E-Box in vitro. (A) Co-immunoprecipitation of an epitope-tagged versions of EsCLK-V5 and MYC-EsCYC/BMAL co-expressed in HEK293 cells. Two experiments (Exp.) are reported showing that precipitates are enriched for EsClock-V5. Membranes were probed with anti-MYC antibody to visualize pulldown efficiencies. For presentation purposes western blot images have been cropped (full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Figure S8A-C). (B,C) EsCLK and EsCYC/BMAL luciferase assay. EsCLK and EsCYC/BMAL - only as a heterodimer - activate the transcription of an E-box luciferase reporter in S2R + and HEK 293 cells, respectively. Cells were transfected with indicated constructs. Negative control set as 1. Data are represented as mean ± SD (n = 3 independent transfections). (D) Identification of conserved domains responsible for the transactivation activity of the EsCLK:EsCYC/BMAL by luciferase assay and their selective deletion. Data are represented as mean ± SD (n = 3 independent transfections). See Supplementary Figure 7 for a schematic representation of the constructs generated. (E,F) Interactions between E. superba’s positive clock elements with those of D. melanogaster and M. musculus evaluated by luciferase assay in S2R + and HEK 293 cells, respectively. Negative control set as 1. Data are represented as mean ± SD (n = 3 independent transfections). Student’s t-test Bonferroni-corrected p-values for all the experimental comparisons discussed were presented in Supplementary Table 3. Statistical significance of the most relevant comparisons were shown as *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.005.