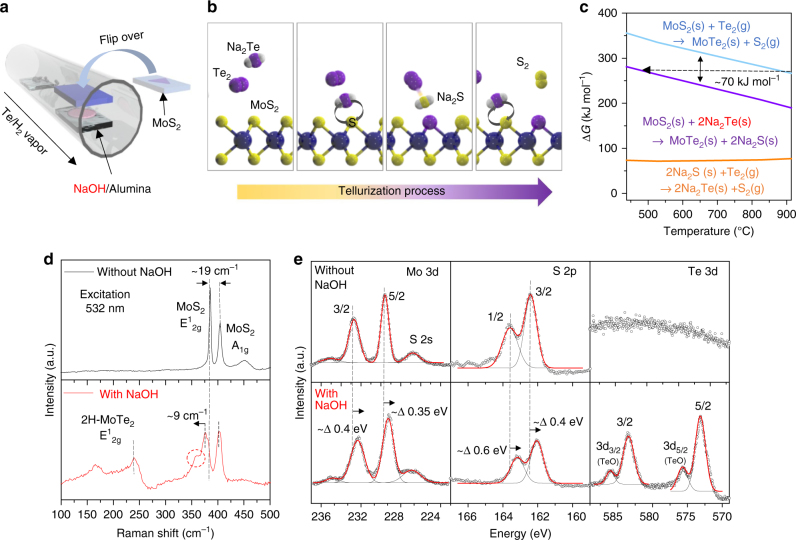
Fig. 1.
Alkali-metal-assisted conversion from MoS2 to MoTe2. a Schematic of the Na-assisted tellurization process. MoS2 was flipped over to face the NaOH-coated substrate. b Illustration for the conversion step from Mo–S to Mo–Te via a Na-scooter. Na2Te, which is regarded as the most probable Na–Te compound from sodium hydroxide, plays a role as the Te carrier and catalyst for exchanging with S atoms. After exchanging S atoms with Te atoms, Na2S is converted to Na2Te under Te-rich conditions. c Gibbs free energy changes for conversion without/with Na-scooter. ∆G is reduced to around 70 kJ mol−1. d, e Raman spectra (d) and XPS taken for Mo, S, and Te (e) of partially tellurized MoS2−xTex without/with Na-scooter at 600 °C for 30 min