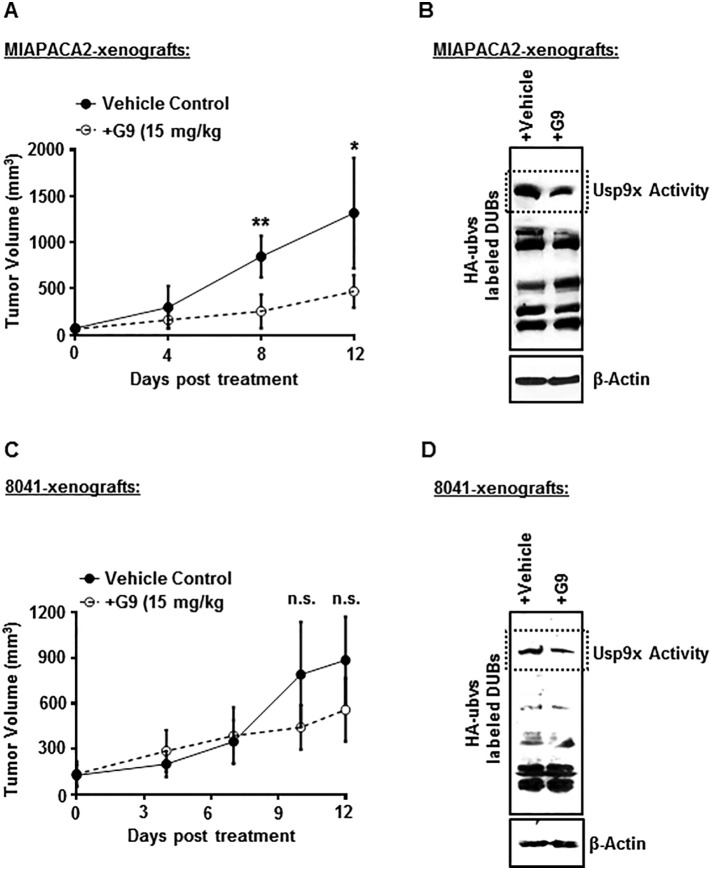
Figure 6.
Small-molecule inhibitor G9 decreases tumor size in human MIAPACA2 xenografts but has no effect on murine 8041 xenografts.
(A) G9 treatment significantly reduces tumor size in human MIAPACA2 xenografts. N = 4 for each group. *P < .05, **P < .005. A total of 5 × 106 MIAPACA2 cells were injected subcutaneously, mid-dorsally in NSG mice. When measurable, tumors were size matched and treated i.p. with either vehicle or 15 mg/kg of G9 every other day for 12 days. Tumor size was monitored, and tumor measurements were recorded.
(B) Immunoblot analysis shows inhibited activity of Usp9x in G9-treated human MIAPACA2-xenograft tumors. Tumor tissue was extracted from vehicle- or G9-treated mice and lysed in DUB assay buffer before incubation with HA-UbVS and immunoblot analysis with anti-HA antibody to detect HA-UbVS–labeled DUBs as a measure of DUB activity (Usp9x activity is denoted). β-Actin was used as the loading control.
(C) G9 treatment showed no significant effect on growth of murine 8041 xenograft tumors. Tumors were established with 2 × 106 8041 cells as described in A. N = 5 for each group.
(D) Immunoblot analysis shows inhibition of Usp9x activity in G9-treated murine 8041-xenograft tumors. β-Actin was used as the loading control.