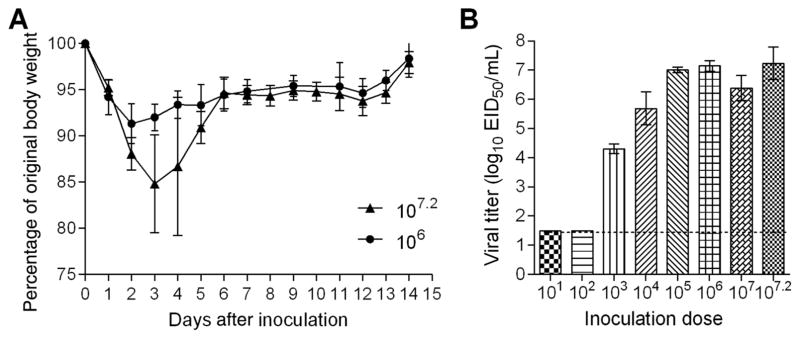
Figure 4.
Pathogenicity of A(H3N2) canine influenza virus in mice. A, Groups of 5 mice were intranasally inoculated with 107.2 or 106.0 50% egg infective doses (EID50) of A/canine/IL/12191/2015 (H3N2) virus and observed for signs of morbidity and mortality for 14 days. The percentage weight loss (±SD) is shown. B, Additional groups of 3 mice were inoculated with 107.2 EID50 or serial 10-fold dilutions ranging from 107.0 to 101.0 EID50 of virus and were euthanized 3 days after inoculation, when lung tissues were collected for viral titer determination. Viral titers are presented as log10 EID50/mL (±SD). The limit of detection is 1.5 log10 EID50/mL.