Figure 3.
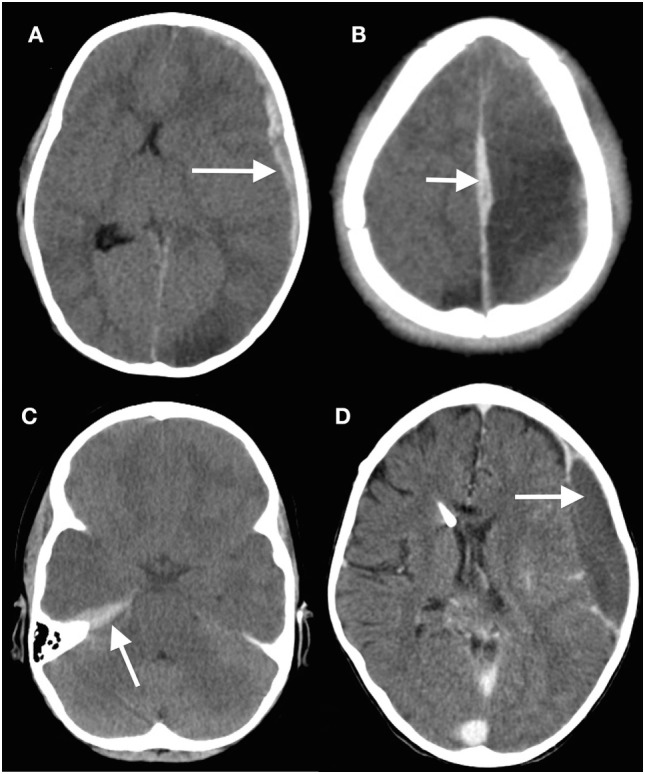
Subdural hematomas in children. (A) Head computed tomography (CT) scan showing a typical acute subdural hematoma with a hypodensity in the ipsilateral posterior cerebral artery territory; (B) interhemispheric subdural hematoma (arrowed) with adjacent venous hypodensity; (C) subtle subdural hematoma situated on the tentorium beneath the temporal lobe; (D) minor knocks to the head can easily cause a subdural hematoma (arrowed) in children with ventriculoperitoneal shunts, especially if there is a degree of overdrainage from the shunt (13) (modified).
