Fig. 1.
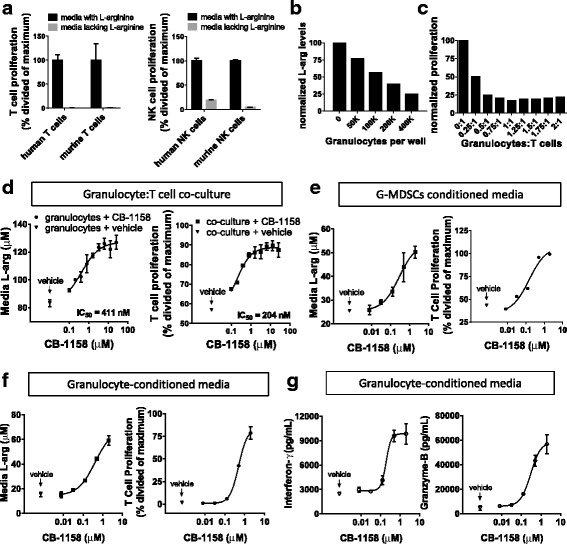
Inhibition of arginase reverses myeloid cell-mediated suppression of in vitro T cell proliferation. a T cells (left) and NK cells (right) require extracellular L-arginine for proliferation. CFSE-loaded T cells or NK cells were stimulated with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 or IL-2, respectively, in media either containing or lacking L-arginine. Proliferation was measured after 72 h by flow cytometry. b Isolated human granulocytes deplete L-arginine from the media, measured after 48 h by LC/MS. c Human peripheral blood T cells are suppressed from anti-CD3/anti-CD28-induced proliferation by co-culture with granulocytes isolated from the same healthy donor. d left, CB-1158 inhibits the consumption of arginine from the media by granulocytes in a dose-dependent manner; right, CB-1158 inhibits granulocyte-mediated suppression of T-cell proliferation in a dose-dependent manner. The ratio of granulocytes to T cells in the co-cultures was 0.25 to 1. e, CB-1158 reverses T cell suppression conferred by granulocytic MDSCs. Media conditioned by granulocytic-MDSCs purified from a lung cancer patient’s blood inhibited T-cell proliferation and is depleted of L-arginine, and both effects are reversed in a dose-dependent manner by CB-1158. Left, arginine amounts in the media; right, T-cell proliferation. The ratio of MDSCs conditioning the media to T cells was 1 to 1. f, Conditioned media from purified granulocytes isolated from a head and neck cancer patient’s blood inhibited T-cell proliferation and are depleted of L-arginine, and both effects are reversed in a dose-dependent manner by CB-1158. Left, arginine amounts in the media; right, T-cell proliferation. The ratio of granulocytes conditioning the media to T cells was 0.5 to 1. g, CB-1158 reverses the inhibition of secretion of interferon-γ and granzyme-B conferred by cancer patient granulocytes. Media from panel (f) were analyzed by Cytometric Bead Array
