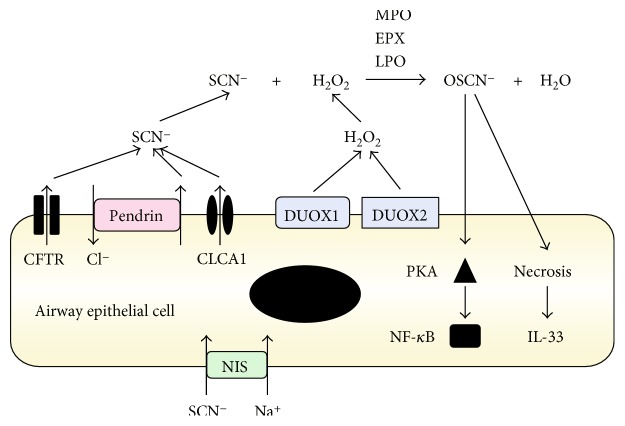
Figure 1.
Schematic model of OSCN− production via the pendrin/DUOX/peroxidase pathway in airway epithelial cells (modified from [9]). In airway epithelial cells, SCN− is actively transported into pulmonary lumens via NIS/SLC5A5 at the basal side and via several anion transporters including CFTR and pendrin/SLC26A4 at the apical side. SCN− together with H2O2 generated by Duox1 and Duox2 is catalyzed by peroxidases into OSCN−. Three peroxidases including MPO, EPX, and LPO are involved in this reaction. A low dose of OSCN− activates NF-κB via PKA, whereas a high dose of OSCN− causes necrosis followed by release of IL-33 in airway epithelial cells. It is of note that if peroxidases are inhibited, it would protect airway epithelial cells against inflammation.