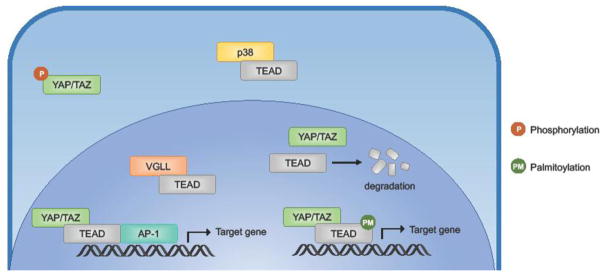
Figure 3. Mechanisms of TEAD regulation.
Several mechanisms have been shown to regulate TEAD transcriptional activity. Coactivator binding is the most important mechanism of altering TEAD transcriptional activity. YAP/TAZ bind TEAD along with AP-1 to activate transcription of downstream target genes. The transcriptional program driven by the YAP/TAZ, TEAD, AP-1 complex has been shown to be important for cancer progression. VGLL has been shown to compete with YAP/TAZ for TEAD binding. Availability of and competition between coactivators drive different TEAD transcriptional programs. Palmitoylation of TEAD in the central hydrophobic pocket is necessary for protein stability and is also suggested to be important for YAP binding. Osmotic stress acts via p38 to induce TEAD cytoplasmic translocation.