Fig. 2.
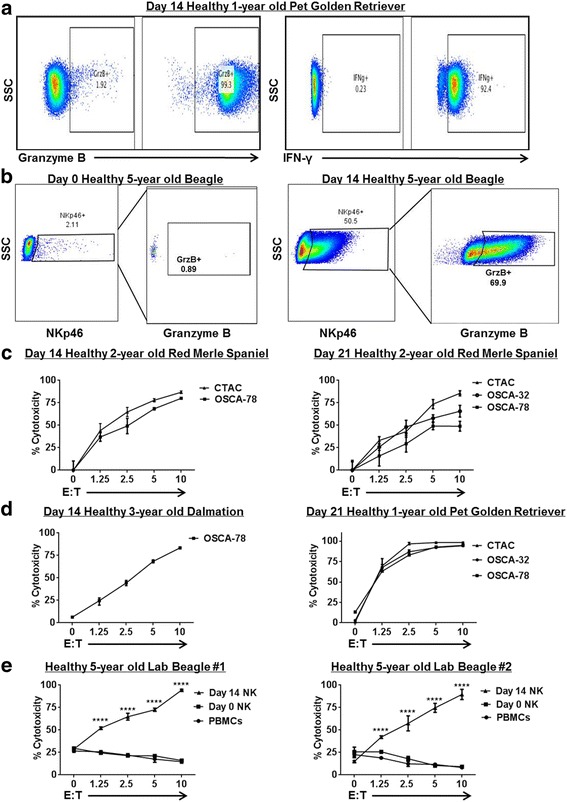
Ex Vivo Expanded Dog NK Cells are Active and Cytotoxic. Dog NK cells were CD5 depleted and co-cultured with lethally irradiated K562 Clone9.mbIL-21 and rhIL-2 (100 U/mL). After 14–21 days, NK cells were assayed by flow cytometry for expression of activation markers and cytotoxicity. a. Day 21 unstimulated cells show strong expression of NK activation markers Granzyme B (left) and interferon-γ (right) compared to isotype controls. In each panel, a representative experiment from a minimum of 3 replicates is shown. b. Post-CD5 depletion, recovered NK cells were assayed at day 0 and at day 14 for expression of NKp46 and activation marker Granzyme B. Immediately post-depletion (Left), there is minimal NKp46 expression with correspondingly absent Granzyme B expression in the NKp46 sub-population. At day 14 (Right), we observed significant upregulation of NKp46 expression with corresponding upregulation of Granzyme B. c. Expanded NK cells from a healthy 2-year old Red Merle Spaniel donor were assayed at day 14 (Left) and day 21 (Right) for cytotoxicity in 12–16 h killing assays with dog-specific tumor cell targets, including the dog NK sensitive CTAC tumor cell line and osteosarcoma cell lines. Dose-dependent cytotoxicity was observed. d. Expanded NK cells from different donors were assayed at day 14 (Left) and day 21 (Right) for cytotoxicity in 12–16 h killing assays. e. Blood samples were obtained at 3 time points from 2 farm beagle donors, and the cytotoxicity of fresh PBMCs (incubated with 100 IU/mL rhIL-2) was compared to CD5-depleted NK cells at day 0 (also incubated with 100 IU/mL rhIL-2) and expanded NK cells at day 14. Mean values ± SD are shown. For each panel, a representative experiment of 1–2 replicates is shown. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001 via one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-test
