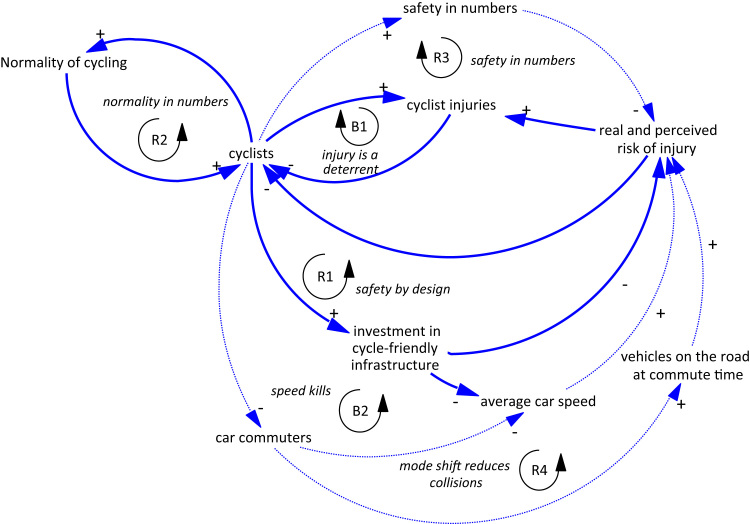
Fig. 1.
Causal loop diagram for commuter cycling in Auckland (Macmillan et al., 2014). Variables in boxes are those whose levels we are interested in following over time (stocks). Arrows with positive signs (+) indicate that a change in the arrow-tail variable leads to a corresponding change in the arrow-head variable. Arrows with a negative sign (-) indicate that a change in the arrow-tail variable leads to an inverse change in the arrow-head variable. R – Reinforcing loop, the result of which is an amplification of the initial pattern of behaviour. B – Balancing loop, the result of which is a dampening of the initial pattern of behaviour). The dashed connection was one where there remained significant uncertainty about the current existence of the relationship. This diagram has been reproduced with permission from http://ehp.niehs.nih.gov/1307250/.