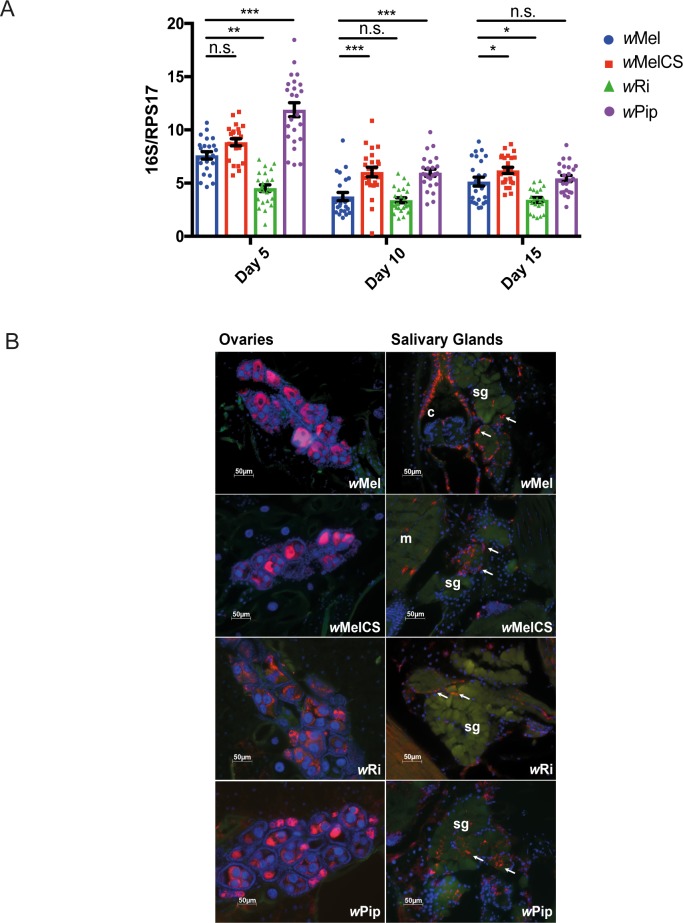
Fig 3. Wolbachia density and distribution in transinfected Ae. aegypti lines.
(A) Density of Wolbachia within 5-, 10- and 15-day old whole female mosquitoes was determined by qPCR using primers directed to the conserved 16S rRNA gene. Density is expressed as the mean ratio between 16S and the Ae. aegypti host rps17 gene. Data are the mean and SEM of 24 mosquitoes. Asterisks indicate significance compared to wMel at each time point (Kruskal-Wallis, Dunn's test with multiple test corrections; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, n.s. not significant). (B) The distribution of wMelCS, wRi and wPip Wolbachia strains in mosquitoes was determined in sections of paraffin-embedded female mosquitoes (5 to 7-day old) using fluorescence in situ hybridisation (FISH). The fluorescently labelled 16S probe detects the 16S rRNA gene from all four Wolbachia strains. Total DNA was stained in blue using DAPI and a green filter was included to increase contrast with surrounding tissues. Sg indicates salivary gland tissue, m indicates muscle, and c indicates cardia. White arrows identify select regions of Wolbachia staining.