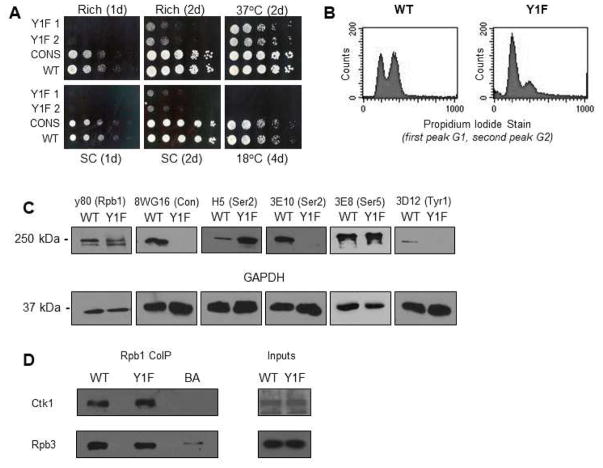
Figure 1. RNAP II CTD Tyr to Phe substitution results in severe growth defects.
(A) Tetrad dissection of heterozygous diploid Y1F CTD strain (Y1F). Y1F CTD in haploid tetrads marked with NAT resistance and is present in all small-size tetrads. Yeast spot assay comparing growth of WT, CONS, and two Y1F clones, with serial fivefold dilutions, on rich or synthetic complete (SC) medium at 30°C, or on rich medium at indicated temperature, for indicated number of days. (B) Cell-cycle assay showing unsynchronized cells stained with propidium iodide, the two peaks representing cells in G1/G0 and G2, respectively. (C) Western blot analysis of cell lysates derived from WT and Y1F strains using antibodies recognizing the N-terminus of Rpb1 (y80), unphosphorylated consensus repeats (8WG16), Ser2P (3E10 and H5), Ser5P (3E8), Tyr1P (3D12) and GAPDH as indicated. (D) Western blot analysis of an Rpb1 co-IP (using y-80), probing for Ctk1 interaction (using 3HA tagged Ctk1 and HA antibody) with RNAP II (normalized to Rpb3). 5% inputs shown. All results shown are representative of three independent experiments.