Figure 3. All genes contributing to the pathways and ontologies most significantly enriched for protein-altering substitutions between nose-colonizing and infection-causing bacteria.
The pathogenesis ontology, in which significant enrichments were observed in infection-causing but not nose-colonizing bacteria, is shown for comparison. Every gene with at least one substitution between nose-colonizing and infection-causing bacteria and which was up- (red) or down- regulated (blue) in one of the pathways or a member of one of the ontologies (blue) is shown. To the left, the number of altering (yellow/orange) and truncating (pink/red) B-class variants is shown, broken down by the population in which the mutant allele was found: nose (BC; yellow/pink) or infection site (BD; orange/red).
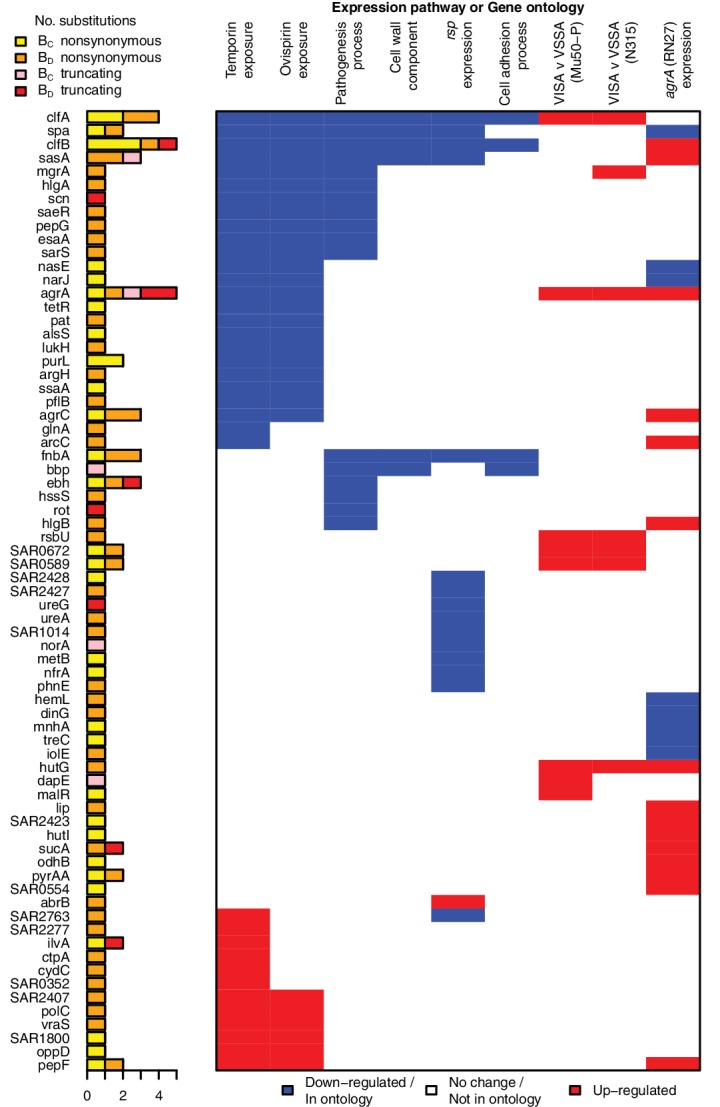
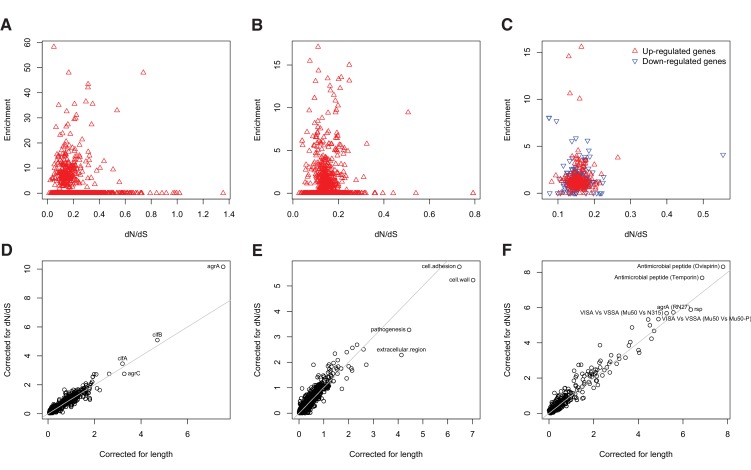
Figure 3—figure supplement 1. Genes enriched for substitutions between nose-colonizing and infection-causing bacteria within patients are not the most rapidly evolving at the species level.