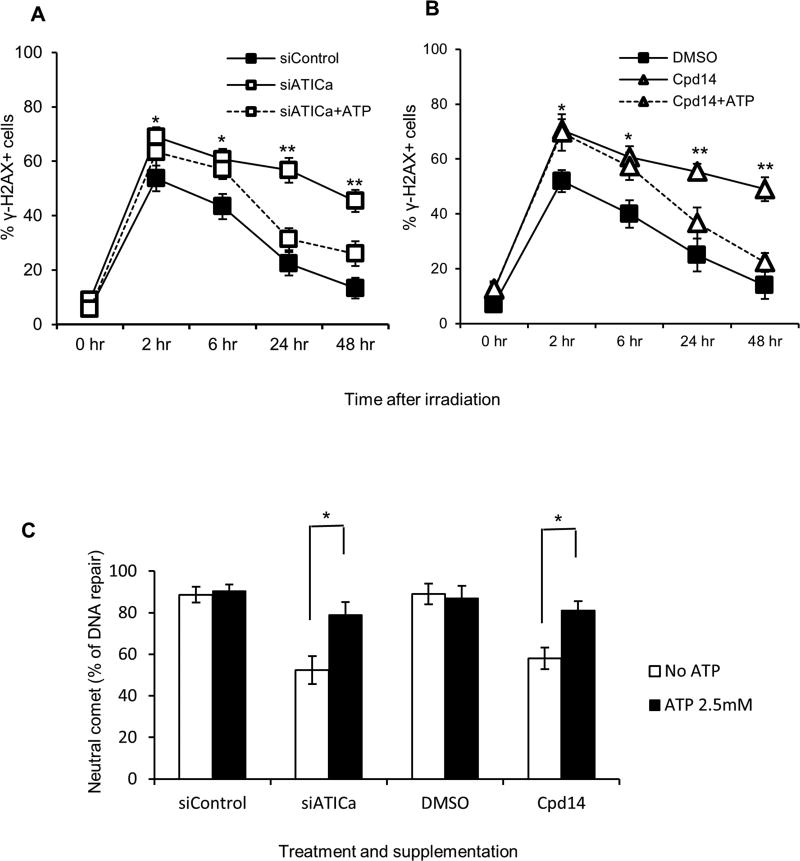
Fig. 6.
ATP supplementation reverses the effects of ATIC inhibition or depletion. (*P < 0.05, **P<0.01, compared to control). (A) HCT116 cells were left untreated (siControl) or pretreated for 48 hours with 30nM siATICa and either not supplemented (siATICa) or supplemented with 2.5mM ATP (siATICa+ATP) one hour prior to irradiation (2 Gy). DSB repair were measured via γH2AX staining assay as described in method section. (B) HCT116 cells were left untreated (DMSO) or pretreated for 48 hours with 1000µM Cpd14 and either not supplemented (Cpd14) or supplemented (Cpd14+ATP) with 2.5mM ATP one hour prior to irradiation (2 Gy). DSB repair were measured via γH2AX staining assay as described in method section. (C) Cells were treated as in (A) and (B), DSB repair was measured via the neutral comet assay as described in method section. Percent repair (% DNA repair) was determined by monitoring the return of the tail moments (TM) of comets to baseline levels ((TM1hrs −TM12 hrs)/TM1hrs). * indicates P<0.05.