Fig. 4.
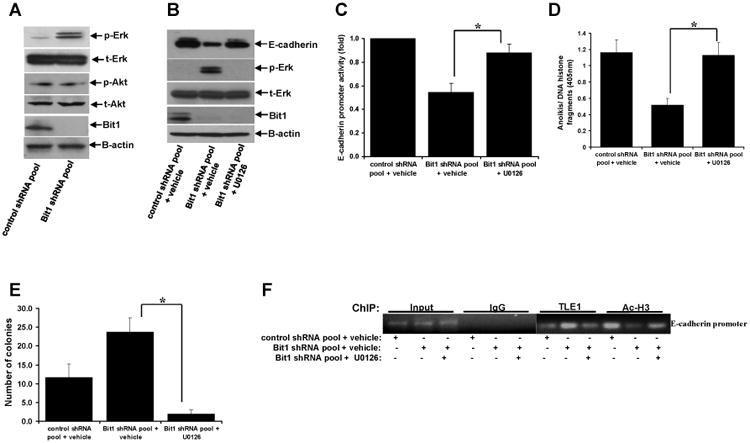
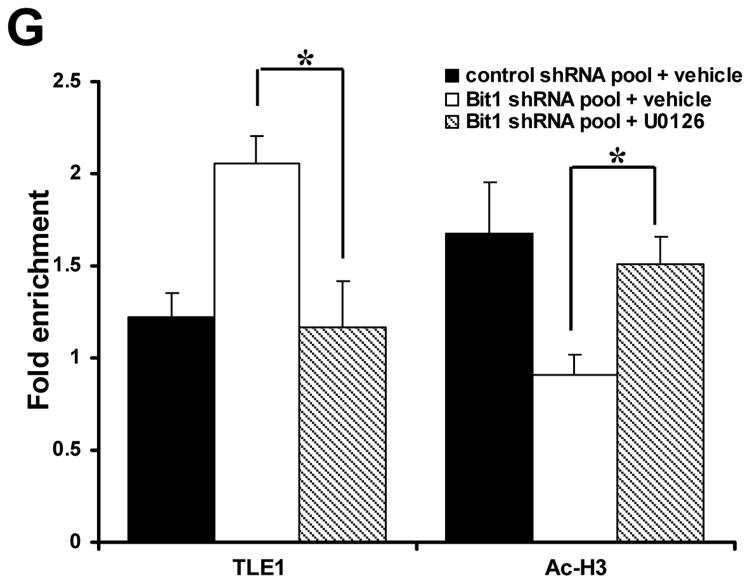
Knockdown of Bit1-induced Erk activation promotes TLE1-mediated transcriptional repression of E-cadherin. A. Control shRNA and Bit1 shRNA pool of BEAS-2B cells were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. B. Control shRNA and Bit1 shRNA cells were treated with U0126 or vehicle as indicated, and 24 h later cells were harvested and cell extracts were prepared and subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. C. Control shRNA and Bit1 shRNA cells were treated with U0126 or vehicle as indicated, and 24 h later cells were subjected to E-cadherin promoter luciferase assay as described in the materials and methods. D. Control shRNA and Bit1 shRNA cells treated with U0126 or vehicle were cultured in suspension for 24 h and then harvested and subjected to Cell Death Elisa assay. E. Control shRNA and Bit1 shRNA cells treated with U0126 or vehicle were subjected to a soft agar assay as described in materials and methods, and the resulting number of colonies was quantified. F. and G. Control shRNA and Bit1 shRNA cells treated with U0126 or vehicle were subjected to ChIP assay. Chromatin was precipitated using ChIP-validated antibodies against TLE1, acetyl-histone H3 (Ac-H3), or control IgG as detailed in the materials and methods. The E-cadherin promoter sequence was amplified by PCR and subjected to agarose gel electrophoresis. The ChIP experiments were repeated at least three times and a representative experiment is shown F. Enrichment of the E-cadherin promoter fragment in TLE1-ChIP and acetyl-histone 3-ChIP over IgG-antibody is shown in G. In C, D, E, and G, three independent experiments were performed in triplicates, *indicates p<0.05 by Student's t test.