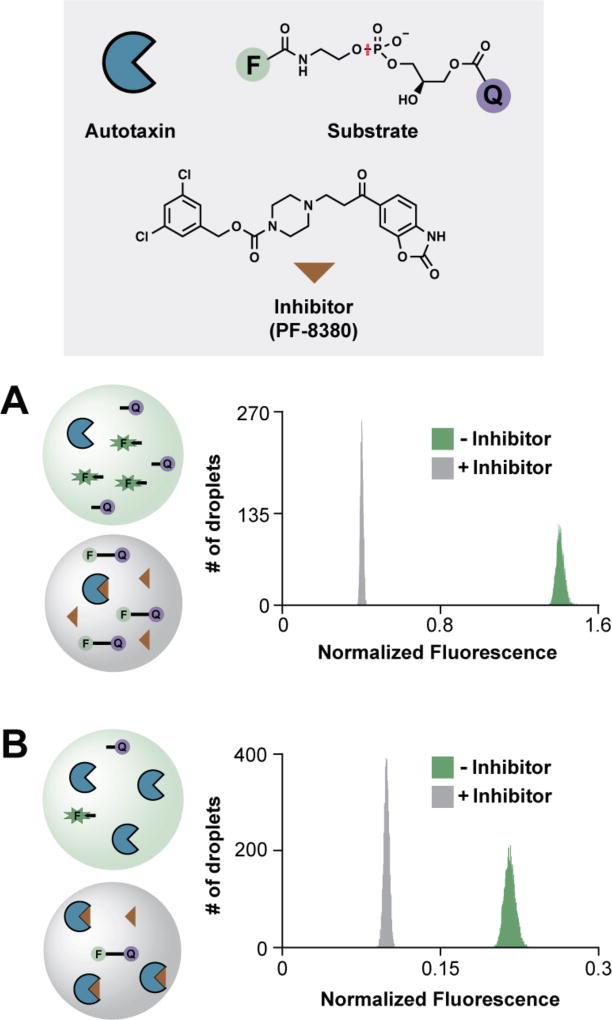
Figure 3. Detection of autotaxin inhibition in ICEcreamer incubators.
(A) Under steady-state conditions, autotaxin (blue pac-man, 50 nM) cleaves fluorogenic phosphodiesterase probe (F–Q, 1.3 µM), liberating fluorescein (green F) from the quencher and increasing droplet fluorescence. The scissile bond is indicated (red). PF-8380 (brown triangle) inhibits autotaxin-catalyzed probe hydrolysis, and droplet fluorescence remains low (Z′ = 0.88). Assays were conducted in the 2×-wide 2×-long ICEcreamer, which incubates droplets for 17.6 min. (B) Under single-turnover conditions, autotaxin (300 nM) rapidly cleaves the probe (100 nM) in the 2×-wide 1×-long ICEcreamer incubator, which incubates droplets for 4.5 min (Z′ = 0.80). Normalized droplet fluorescence was taken as the ratio of signal in the 520- and 570-nm channels (probe:standard). Each histogram represents 5,000 droplets.