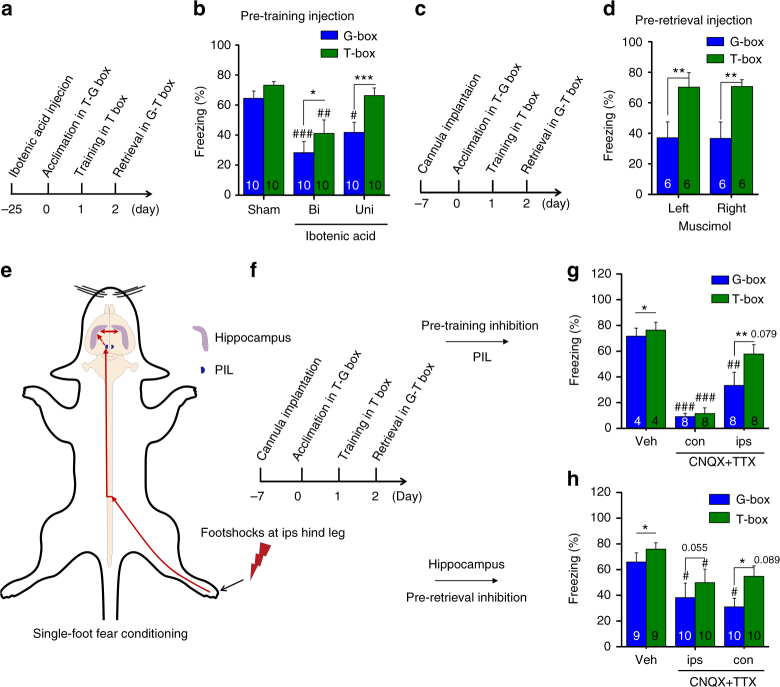
Fig. 2.
Bilateral CA1 are required symmetrically for generalization. a Paradigm for studying CA1 lesion effects by using ibotenic acid. b Unilateral (Uni) CA1 lesion impaired generalization, but bilateral (Bi) CA1 lesion impaired both fear memory and generalization relative to Sham control. c Paradigm for studying inhibition effects of CA1. d Inhibition of left or right CA1 before retrieval tests by using muscimol impaired generalization near equally. e, f Schematic of single-foot fear conditioning and studying paradigm. g Inhibition of ipsPIL before fear conditioning by using CNQX + TTX impaired generalization, with nonsignificant effect on fear memory relative to Veh, but that inhibiting conPIL impaired both fear memory and generalization. h Using this single-foot paradigm, however, inhibition of ipsCA1 or conCA1 before retrieval tests impaired generalization similarly, while ipsCA1 or conCA1 inhibition caused nonsignificant reduction of fear memory relative to Veh. Statistical comparisons are performed by using two-way ANOVA (*contrast effects for G-box vs. T-box; #parameter estimates for control vs. treatment); * or # P < 0.05, ** or ## P < 0.01, *** or ### P < 0.001. Error bars, s.e.m. PIL, the posterior intralaminar nuclei of the thalamus. Veh, vehicle; ips, ipsilateral; con, contralateral