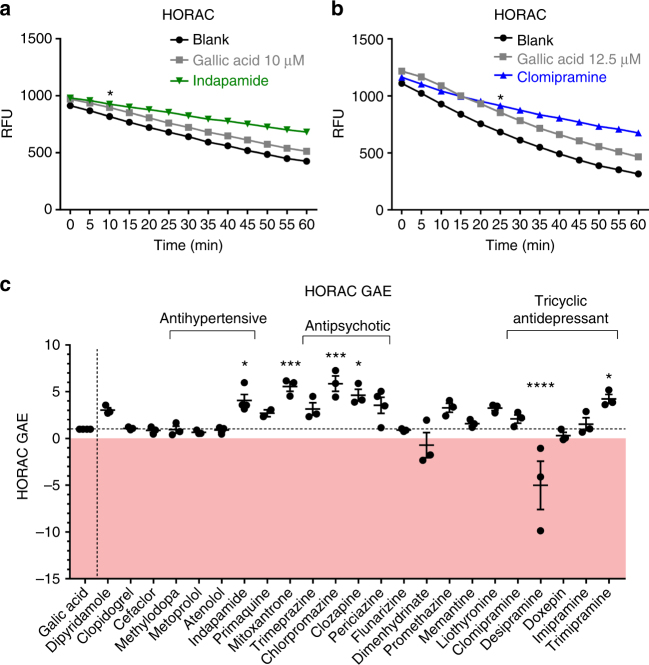
Fig. 4.
Scavenging of hydroxyl radicals in a biochemical assay. The antioxidative capacities of selected compounds that reduced iron-mediated neurotoxicity were analyzed using the HORAC assay. a shows a representative experiment depicting the decay of relative fluorescence units over 60 min for indapamide, gallic acid (GA) and the control (blank). b The upward shift of the curve for clomipramine in the HORAC assay indicates an antioxidative effect that is even stronger than gallic acid. HORAC gallic acid equivalents (GAEs) were calculated by the integration of the area under the curve of the decay of fluorescence of the test compound over 60 min in comparison to 12.5 µM gallic acid and blank. Shown are data of n = 3–4 independent experiments ±SEM, with each experiment performed in triplicates (c). The antipsychotics showed strong antioxidative effects, as demonstrated with HORAC GAEs of >3. Data points >1 represent antioxidative capacity (the gallic acid effect is 1), 0 represents no antioxidative properties, and data <0 show pro-oxidative effect. Two-way ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple comparisons test as post hoc analysis (a, b); the first significant time point vs. gallic acid is depicted as asterisk. One-way ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple comparisons test as post hoc analysis vs. gallic acid (c). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001. RFU relative fluorescence units