Figure 1.
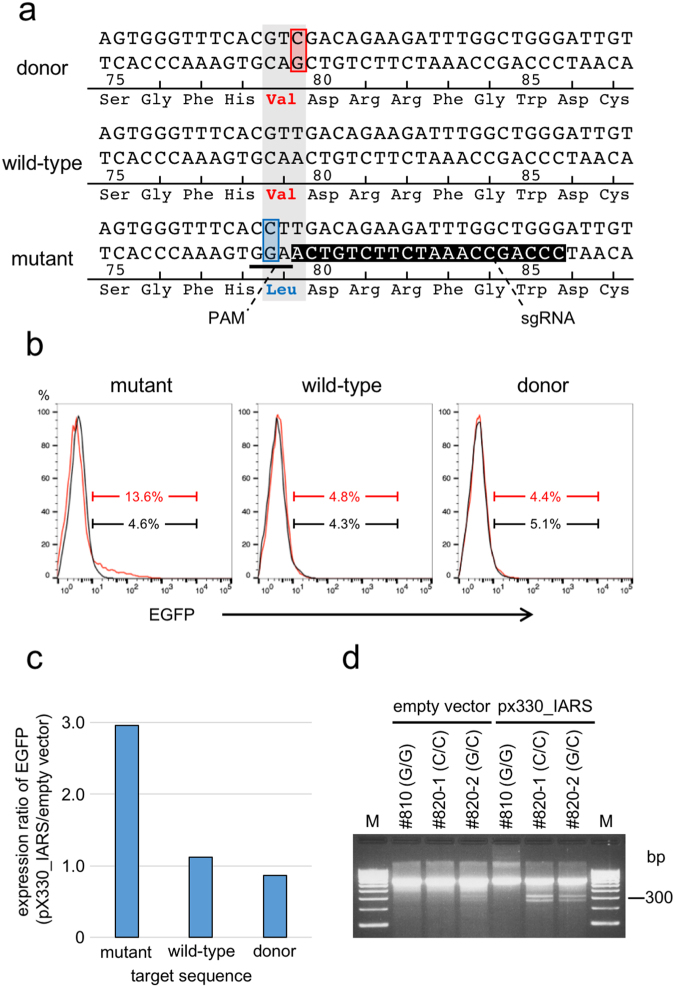
Design of the CRISPR/Cas9 single guide RNA and assessment of target specificity. (a) Sequence of the region that flanks the mutation site in IARS. The base at the third position of the codon that encodes p.Val79 was changed in the donor DNA from thymine to cytosine. The PAM sequence (underlined) is located at nucleotides 236 A to 234 G on the bottom strand of the IARS gene and includes the substituted nucleotide 235 G. Inverted characters show the sgRNA. (b) Flow cytometric analysis of the target specificity of CRISPR/Cas9. The empty vector pX330 (black line) or pX330_IARS (red line) was introduced into HEK293T cells with the vector p2color that contained either the mutant, wild-type or donor target sequence. The histogram shows the expression of EGFP in tdsRed positive cells. (c) Comparison of the expression of EGFP for different target sequences. The values are shown as the expression ratios of EGFP when each p2color vector was introduced with the empty vector or pX330_IARS. (d) Cleavage frequencies in the T7E1 assay in BFF cells derived from #810 (G/G wild-type), #820-1 (C/C homozygous mutant), and #820-2 (G/C heterozygous mutant). M indicates DNA size marker (100 bp ladder).