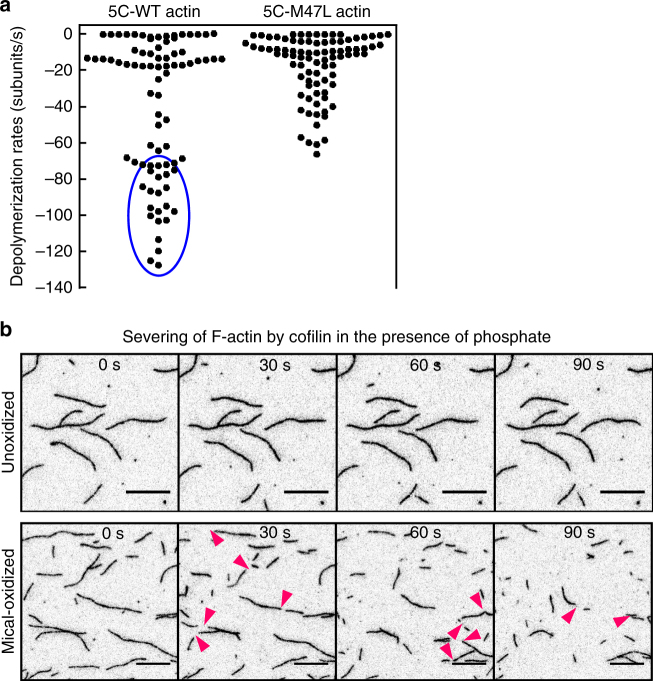
Fig. 3.
Mical oxidation of both M44 and M47 residues on actin drives its catastrophic disassembly and cofilin severing. a Mical oxidation of both—M44 and M47—contributes to F-actin destabilization. Single filament depolymerization rates of 5C-WT and 5C-M47L 2 min after addition of Mical (10 nM) and NADPH (0.1 mM) into the flow chamber. Rates were determined from the TIRF movies (n = 3 samples per condition). Two independent preps of each actin form (WT and M47L) were tested. Rates corresponding to the catastrophic disassembly events are encircled in blue. b Mox-F-actin in the presence of inorganic phosphate (Pi) (12.5 mM) is rapidly severed and disassembled by cofilin. Cofilin-induced actin disassembly is very slow in unoxidized actin (top panel) and no severing events were observed. Note, that cofilin-mediated disassembly is extensive in ADP-Pi-Mox-F-actin (bottom panel) (also compare to the Supplementary Fig. 2a). Severing events are indicated by magenta arrowheads. Bar = 10 µm