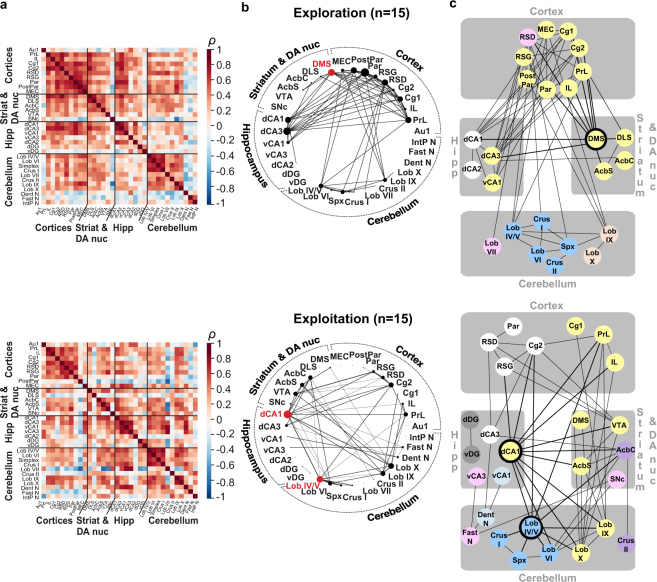
Figure 2.
Functional network of the acquisition of a sequence-based memory. (a) Inter-regional correlation matrices for exploration (top) and exploitation (bottom) mice, each normalized to their respective controls. Axes correspond to brain structures. Colours reflect correlation strength (scale, right). (b) Network graphs generated by considering only the strongest correlations (Spearman’s ρ ≥ 0.64, p ≤ 0.01), with the thickness of the connections proportional to correlation strength and node size proportional to degree. Network hub structures are highlighted in red. The exploration mice’s network appears to be centred around cortical correlations with striatal, hippocampal and cerebellar structures, with the dorso-medial striatum as a network hub. The exploitation network is dominated by hippocampo-cerebellar correlations, with two network hubs, the hippocampal dorsal CA1 and cerebellar lobules IV/V. (c) Markov clustering algorithm was applied to organize brain structures into discrete color-coded modules based on their common inter-connections. Network hubs are highlighted in black. Consistent with the network graph analysis, the clustering in the exploration network revealed a major cortico-striatal cluster with the hub (in yellow), also containing hippocampal regions, and alongside three regionally confined clusters (a hippocampal cluster and two cerebellar clusters). In the exploitation network, the clustering revealed an interregional cluster with cortical, striatal, hippocampal and cerebellar structures (in yellow), alongside a cortico-hippocampal cluster (in white) and several other inter-regional clusters. The two exploitation network hubs (highlighted in black) belong to two different clusters and are at the interface of several other clusters, illustrating their central position in the network. Abbreviations: cortex: primary auditory (Au1), prelimbic (PrL), infralimbic (IL), cingulate 1 and 2 (Cg1, Cg2), dysgranular and granular retrosplenial (RSD, RSG), parietal and posterior parietal (Par, PostPar), medial entorhinal (MEC); striatum and dopaminergic nuclei (DA nuc): dorsomedial striatum (DMS), dorsolateral striatum (DLS), nucleus accumbens core (AcbC) and shell (AcbS), ventral tegmental area (VTA), substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc); hippocampus: dorsal CA1 (dCA1), dorsal CA3 (dCA3), ventral CA1 (vCA1), ventral CA3 (vCA3), dorsal CA2 (dCA2), dorsal and ventral dentate gyrus (dDG, vDG); cerebellum: lobules IV/V (Lob IV/V), VI (Lob VI), VII (Lob VII), IX (Lob IX), X (Lob X), Simplex (Spx), dentate (Dent N), fastigial (Fast N) and interpositus nuclei (IntP N).