Table 2.
Propargylation of aldehydes catalyzed by 1-Cr a
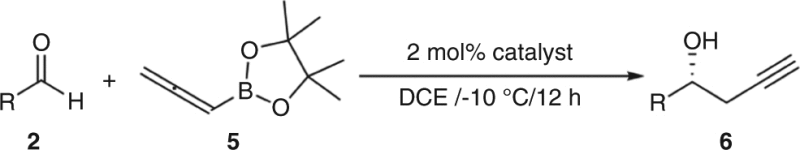
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | R | Catalyst | Yield (%)b | ee (%)c |
| 1 | Ph | 1-Cr | 92 | 92 (R) |
| 2d | Ph | Homo | 81 | 0 |
| 3 | 4-MeOPh | 1-Cr | 96 | 96 (R) |
| 4d | 4-MeOPh | Homo | 78 | 0 |
| 5 | 4-ClPh | 1-Cr | 93 | 92 (R) |
| 6 | 4-BrPh | 1-Cr | 91 | 92 (R) |
| 7 | 4-NO2Ph | 1-Cr | 94 | 91 (R) |
| 8 | 4-COOMePh | 1-Cr | 92 | 94 (R) |
| 9 | 3-MeOPh | 1-Cr | 90 | 99 (R) |
| 10 | 1-Naphthyl | 1-Cr | 92 | 93 (R) |
| 11 | PhCH=CH | 1-Cr | 90 | 97 (R) |
| 12 | DBBA | 1-Cr | 0 | 0 |
| 13d | DBBA | Homo | 90 | 0 |
DBBA: 3,5-dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde
a Reaction conditions: 2 (0.10 mmol), 5 (0.15 mmol), and (S)-1-Cr (2 mol% catalyst based on MOF) in DCE (0.8 mL), −10 °C, 12 h
b Isolated yield
c Determined by chiral HPLC analysis (letters in brackets specify the excess isomer)
d A 1:1 mixture of Cr(acac)3 and (S)-Me2 L (6 mol% catalyst based on Cr) was used as the catalyst
