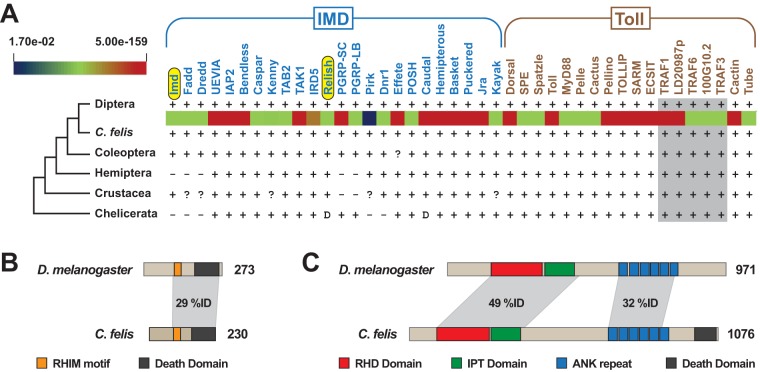
FIG 4.
IMD and Toll signaling pathways are conserved between Drosophila and C. felis. (A) C. felis contains homologs to D. melanogaster IMD (n = 24) and Toll (n = 18) pathway genes. D. melanogaster genes were used as queries in reciprocal best blastn searches against the C. felis 1KITE transcripts. E-values for matches are depicted by a heat map between C. felis and Diptera (at the top is the range of E values across all significant hits). The distribution of these genes in other arthropod genomes is shown as follows: −, absent from lineage; ?, uncertain homology; and D, divergent architecture. Gray shading indicates that tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) homologies were not confidently assigned outside the C. felis/D. melanogaster comparisons. (B and C) Comparison of Drosophila and C. felis proteins encoded by Imd (B) and Relish (C). C. felis proteins were translated from transcripts identified by tblastn searches against the C. felis 1KITE transcripts using the proteins encoded by D. melanogaster Imd (NCBI accession no. NP_573394) and Rel (NP_477094). Protein domains were predicted using the SMART database (54): RHD, Rel homology DNA binding; IPT, ig-like, plexins, transcription factors; ANK, ankyrin. The Rip homotypic interaction (RHIM) motif was demarcated as previously characterized (53).