FIG 2.
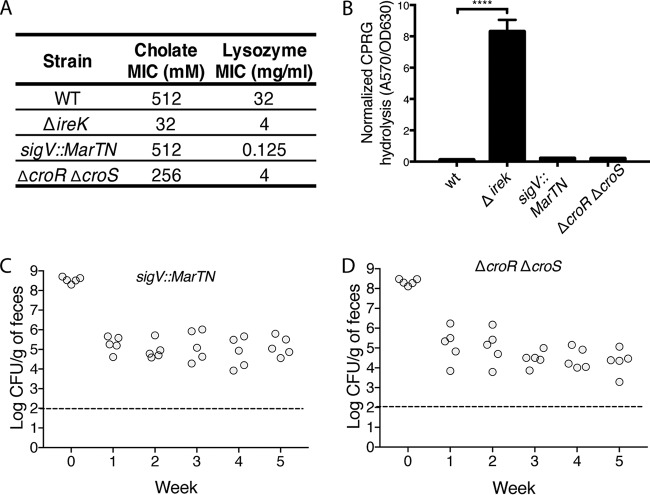
Loss of lysozyme resistance alone does not cause the ΔireK colonization defect. (A) Cholate resistance was determined for the WT E. faecalis strain (OG1RF), the cholate-sensitive ΔireK (CK119) and ΔcroR ΔcroS (SB6) mutants, and the sigV transposon mutant (35H2). The reported MICs represent the median values from three independent biological replicates. (B) CPRG hydrolysis was measured for the strains listed in panel A. The reported measurements represent averages from three independent cultures, and error bars represent standard deviations. Statistical significance was evaluated by t test. ****, P < 0.0001 versus WT. (C and D) Intestinal colonization of the lysozyme-sensitive mutants listed in panel A. Groups of 5 mice were colonized with either the ΔireK mutant or one of the tested lysozyme-sensitive mutants. Colonization levels were determined by enumerating the enterococci in feces by culture on rifampin-supplemented BHI agar. Dashed lines, the limit of detection.