FIG 1.
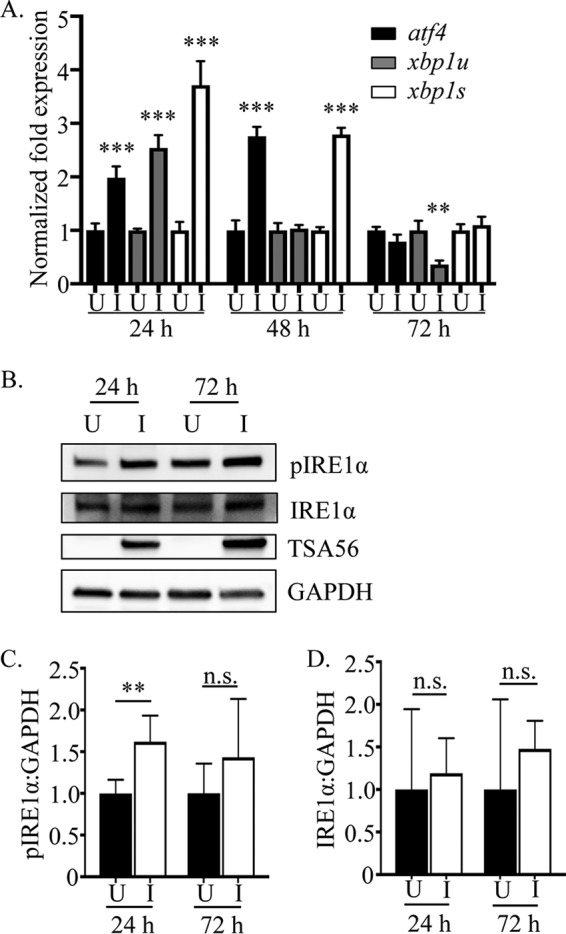
O. tsutsugamushi induces and benefits from ER stress in an amino acid-dependent manner. (A) O. tsutsugamushi infection induces UPR gene expression. Total RNAs isolated from O. tsutsugamushi-infected HeLa cells were subjected to qRT-PCR using primers targeting transcripts of ER stress-regulated genes. Relative mRNA levels of atf4, xbp1s, and xbp1u in infected samples (I) were normalized to gapdh gene transcript levels using the 2−ΔΔCT method. These values were normalized to those of mock-infected (U) samples at each respective time point. Results are representative of at least three separate experiments performed in triplicate. (B) Whole-cell lysates of mock-infected or O. tsutsugamushi-infected cells were analyzed by Western blotting and screened with antibodies specific for phosphorylated IRE1α, IRE1α, TSA56, or GADPH. (C and D) Densitometry was performed on blots from six separate experiments. Statistically significant values are indicated: **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; n.s., not significant.
