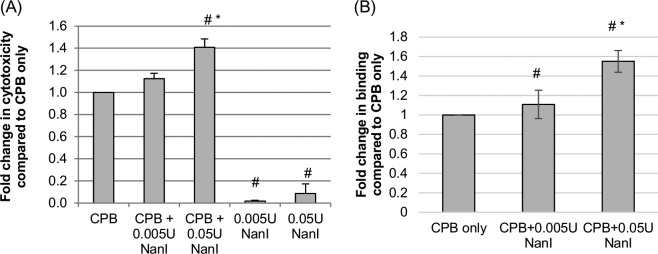
FIG 2.
Effects of NanI on the cytotoxic activity and binding of CPB. (A) CPB-induced cytotoxicity. HUVEC monolayers were grown to confluence and pretreated for 1 h at 37°C with buffer or buffer containing purified native NanI at the concentrations indicated. After these pretreatments, the HUVEC monolayers were rinsed with HBSS twice and then treated with 1.0 μg/ml of purified CPB for 4 h at 37°C. Following this challenge, the supernatant was collected, and relative cytotoxicity was determined by LDH release. (B) Analysis of CPB binding. To determine if the enhanced cytotoxicity observed with NanI pretreatment of HUVECs involved increased toxin binding, HUVEC monolayers were pretreated for 1 h at 37°C with buffer or buffer containing purified native NanI at the concentrations indicated, rinsed twice with HBSS, and then treated for 1 h at 4°C with HBBS or HBSS containing 5 μg/ml of CPB. The monolayers were then washed 3 times at 4°C, and an anti-CPB mouse monoclonal antibody was applied for overnight incubation at 4°C. After two washes with HBSS, an Alexa Fluor 488-labeled anti-mouse IgG antibody was applied for 30 min at room temperature. After 3 washes, fluorescence was quantified by using a plate reader. All experiments were performed at least in triplicate, and the means are presented. Error bars show standard errors of the means (A) or standard deviations (B). # indicates a significant (P < 0.05) difference compared to cells pretreated with buffer prior to treatment with CPB, and * indicates a significant (P < 0.05) difference between cells treated with 0.05 U/ml and those treated with 0.005 U/ml of NanI.