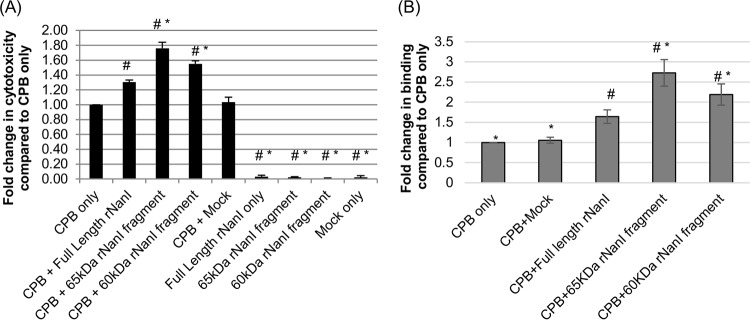
FIG 7.
Effects of rNanI species on CPB binding and cytotoxicity. (A) CPB-induced cytotoxicity. Confluent HUVEC monolayers were pretreated with buffer or buffer containing either 0.05 U/ml of full-length rNanI or an equimolar concentration of the other two rNanI species for 1 h at 37°C. The pretreated monolayers were rinsed twice with HBSS and then challenged with 1 μg/ml of purified CPB for 4 h at 37°C. The culture supernatant was collected, and relative cytotoxicity was determined by LDH release. (B) Analysis of CPB binding. To determine if the enhanced CPB cytotoxicity observed in panel A was due to increased CPB binding, HUVEC monolayers were pretreated with buffer or buffer containing either 0.05 U/ml of full-length rNanI or an equimolar concentration of the other two rNanI species for 1 h at 37°C, washed twice with HBSS, and then challenged for 1 h at 4°C with HBSS or HBSS containing 5 μg/ml of CPB. The monolayers were washed 3 times at 4°C, and an anti-CPB mouse monoclonal antibody was added for overnight incubation at 4°C. After two washes with HBSS, an Alexa Fluor 488-labeled anti-mouse IgG antibody was applied for 30 min at room temperature. After 3 washes, fluorescence was quantified by using a plate reader. All experiments were performed at least in triplicate, and the means are presented. Error bars depict standard errors of the means (A) or standard deviations (B). # indicates a significant (P < 0.05) difference compared to cells pretreated with buffer prior to CPB treatment. * indicates a significant (P < 0.05) difference compared to cells treated with full-length rNanI before CPB treatment.