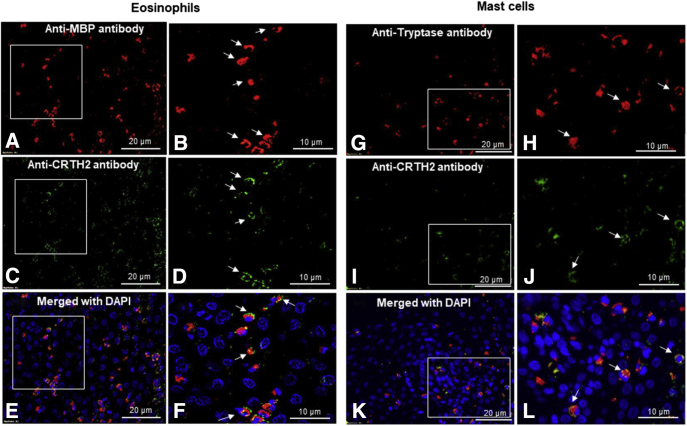
Supplementary Figure 2.
CRTH2 receptor is expressed on the eosinophils and tissue-accumulated mast cells in the esophageal biopsy specimen of human EoE. The in vitro analysis indicated that VIP-receptor CRTH2 is critical for eosinophil motility. Therefore, we examined whether tissue eosinophils in human EoE similarly express CRTH2 receptors. Accordingly, immunofluorescence analysis was performed using anti-CRTH2 receptor on anti-major basic protein–positive tissue eosinophils in human EoE biopsy specimens. (A and B) The anti-major basic protein– and (C and D) anti-CRTH2–expressed eosinophils are detected in the biopsy specimens of human EoE (A–D, original magnification, 400× and 1000×). The merged photomicrograph of anti-major basic protein– and anti-CRTH2–stained and 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI)-mounted tissue sections show that tissue eosinophils expressed VIP-receptor CRTH2 in the esophageal biopsy specimens of human EoE patients (E and F, original magnification, 400× and 1000×). Furthermore, induced mast cell numbers and their role in the pathogenesis of EoE is well established.4, 13 However, it is not clear which chemokine receptors are responsible for mast cell recruitment in human EoE. Therefore, we examined VIP-receptor CRTH2 expression on the tissue-accumulated mast cells in the esophageal biopsy specimens of human EoE by performing immunofluorescence analyses using antitryptase and anti-CRTH2 antibodies. We showed the presence of antitryptase-positive mast cells in the (G and H) esophageal biopsy specimens and (I and J) CRTH2-stained receptors. (K and L) A DAPI-mounted merged tissue section detected the co-localized tryptase-expressed mast cell expressing CRTH2 receptor in esophageal biopsy specimens of EoE patients. The arrows indicate tissue-accumulated mast cells and CRTH2 receptors on mast cells in respective photomicrographs. The photomicrographs presented are (A, C, and E) 400× and (B, D, and F) 1000× of the original magnification photomicrographs presented. Data are expressed means ± SEM (n = 6–7).