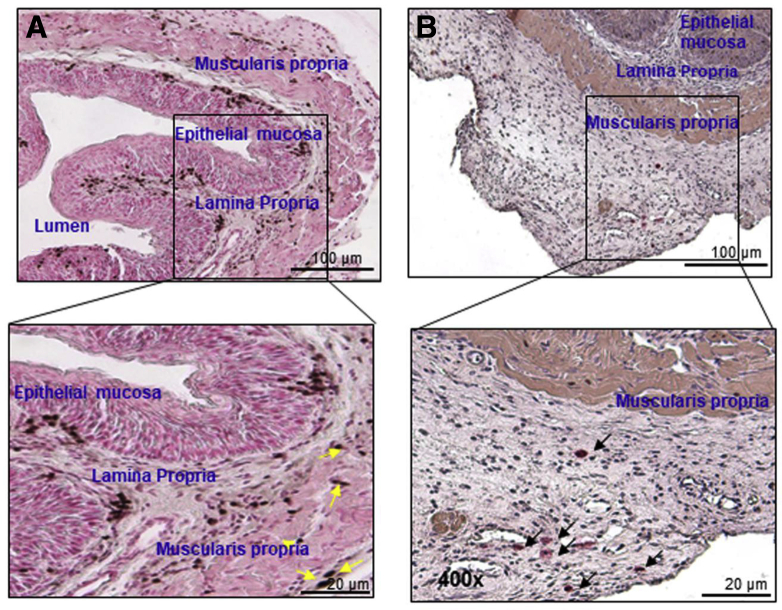
Supplementary Figure 3.
Accumulation of eosinophils and mast cells in muscular mucosa after the induction of experimental EoE. Induced eosinophils and mast cell accumulation is implicated in the induction of esophageal functional abnormalities, including stricture and motility dysfunction in human and experimental EOE.14 However, the accumulation and mechanism of eosinophils and mast cells beyond the epithelial mucosa has not been examined. Because it is difficult to obtain deep mucosal biopsy specimens in human EoE, we examined the accumulation of eosinophils and mast cells in each segment of the mouse esophagus in experimental EoE. The mouse esophageal tissue sections were examined for eosinophils and mast cells after anti-MBP and chloroacetate esterase staining, respectively. Both eosinophils and mast cells were detected in each segment of mouse esophagus after the induction of experimental EoE. (A) A number of eosinophil accumulations in low and high magnification are shown in the epithelial mucosa, lamina propria, and muscular mucosa. Yellow arrows indicates accumulation of eosinophils. (B) Similarly, mast cell accumulation in low and high magnification is shown mostly in the lamina propria and muscular mucosa. Black arrows indicates accumulation of mast cells. Photomicrographs presented are 100× and 400× original magnification, respectively.