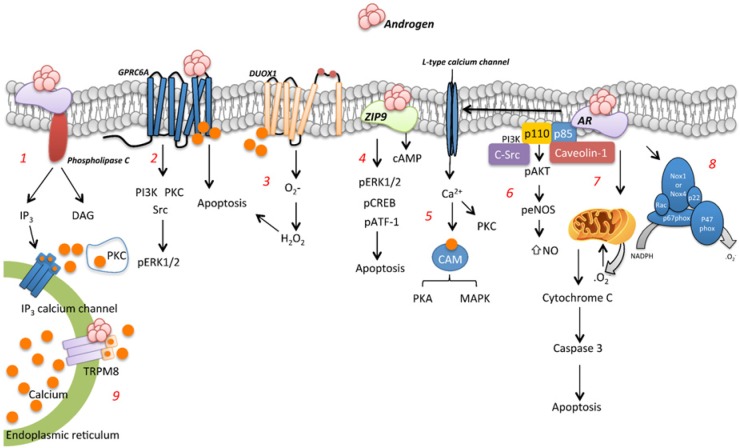
Figure 1. DNA binding-dependent signalling induced by androgens.
(1) The genomic AR signalling involves androgen crossing the plasma membrane, entering the cytoplasm, dissociation of chaperone proteins and binding to the AR. (2) Testosterone induced-ROS generation is followed by an increase in Nox1 and Nox4 mRNA levels and p47phox protein expression. (3) Gas6 signalling induced by testosterone is mediated by phosphorylation of the PI3K/Akt pathway, and an increase of anti-apoptotic Bcl2 family proteins. (4) Hypertrophy induced by testosterone involves recruitment of NFAT through calcineurin activation and GSK-3β inhibition. (5) Testosterone down-regulates the AT2R receptor via AR-mediated ERK1/2 activation. (6) Hypogonadism is shown to decrease nNOS and α-actin expression and increase p38 phosphorylation and caspase 3 cleavage. (7) Testosterone stimulation results in a concurrent increase in the production of H2S, and consequently vasodilation via TRPV4 and large-conductance Ca2+-activated K-channels.