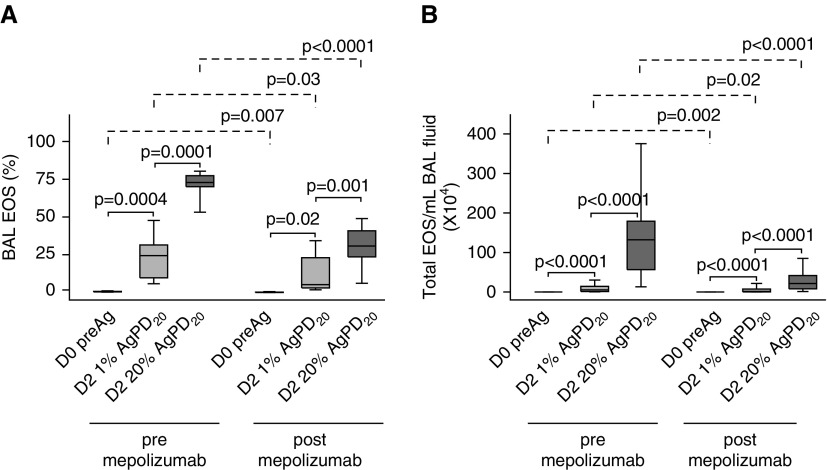
Figure 3.
Mepolizumab decreases, but does not eliminate, allergen-induced bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) eosinophils. Both before and after mepolizumab, there was an antigen dose–dependent increase in the percentage of BAL eosinophils (A) and total numbers of BAL cells per milliliter of BAL fluid (B) 48 hours (D2) after segmental bronchoprovocation with allergen. The magnitude of the antigen-induced eosinophilia was significantly lower after mepolizumab. Data represent medians with first and third quartiles; whisker lines represent the 10th and 90th percentiles (n = 10). P values for pre- versus post-1% and post-1% versus 20% segmental bronchoprovocation with allergen are indicated above the solid lines; pre- versus postmepolizumab P values are indicated above the dashed lines. AgPD20 = allergen provocation dose resulting in a 20% reduction in FEV1; D0, D2 = Day 0, Day 2; EOS = eosinophils; preAg = before antigen administration.