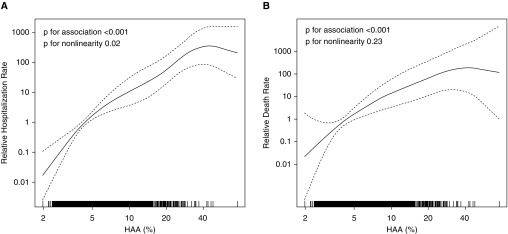
Figure 1.
Continuous associations between high-attenuation areas (HAA) and (A) interstitial lung disease (ILD) hospitalization and (B) ILD mortality. Models are adjusted for total volume of imaged lung; percent emphysema; and generalized propensity score 2, which included age, sex, race/ethnicity, smoking status, cigarette pack-years, body mass index, waist circumference, height, educational attainment, study site/scanner, glomerular filtration rate, radiation dose, alcohol use, total intentional exercise (metabolic equivalent min/wk), coronary artery calcium, diabetes medication use, insulin use, fasting glucose, hypertension, antihypertensive medication use, systolic and diastolic blood pressures, cholesterol medication use, total and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels, C-reactive protein, d-dimer, and cancer history. Solid line is the overall effect estimate, and dashed lines are the 95% confidence bands. Each vertical hash mark in the rug plot along the x-axis represents one study participant.