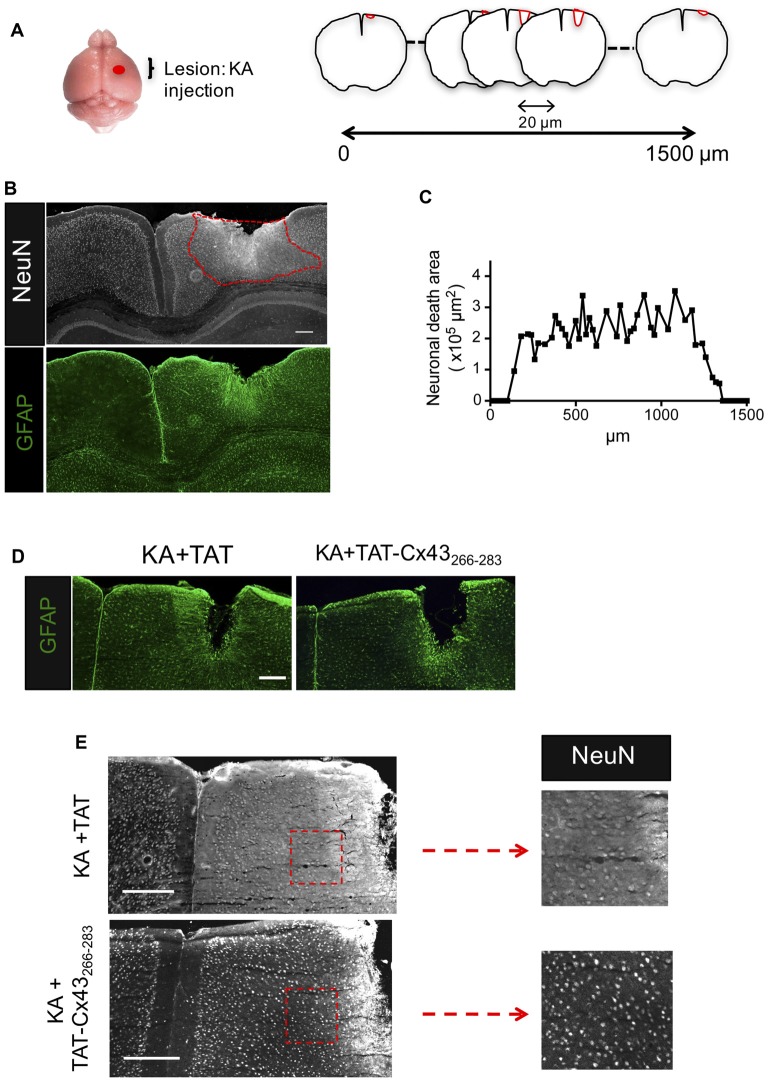
Figure 1.
Effect of TAT-connexin43 (Cx43)266–283 on NeuN and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) expression in adult mouse brain after kainic acid (KA) injection. (A) Schematic of the experimental strategy used to analyze neuronal injury promoted by 1 nmol/μl KA injection. (B) Expression of NeuN and GFAP in the cortex, 7 days after KA injection. Representative photomicrographs from the same field at the level of the lesioned area delimited by the dashed red line. (C) Quantification of neuronal death area along the rostrocaudal axis. Representative photomicrographs of GFAP (D) and NeuN (E) immunohistochemical staining in brain sections at the level of the lesioned area, 7 days after the injection of 1 nmol/μl KA + 1 nmol/μl TAT or 1 nmol/μl KA + 1 nmol/μl TAT-Cx43266–283. Higher magnification photomicrographs showing the decrease in NeuN-positive cells after the injection of KA+TAT compared to KA+TAT-Cx43266–283. Bar, 250 μm.