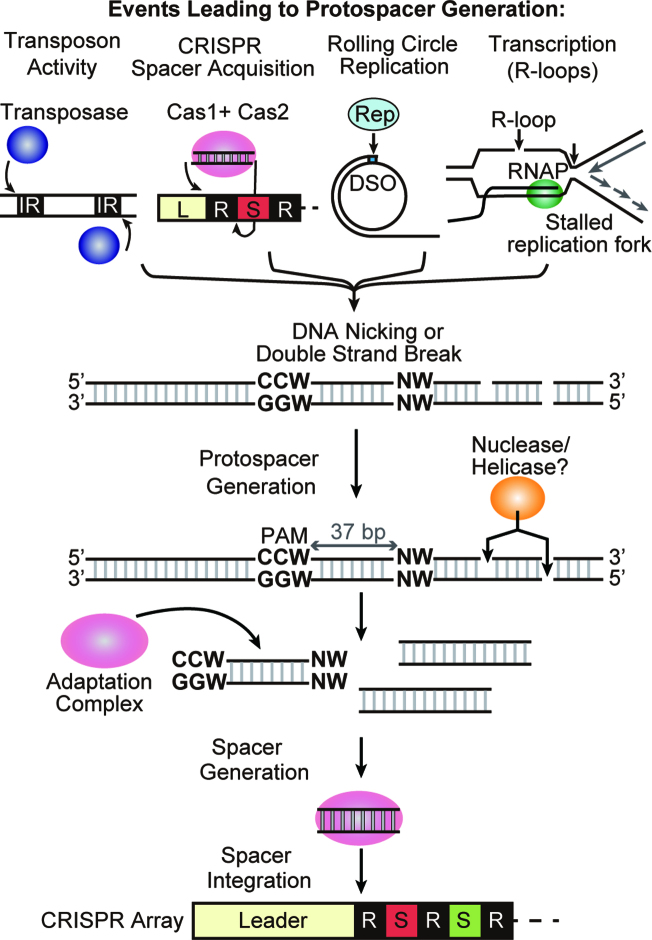
Figure 8.
Model for spacer acquisition in P. furiosus. DNA nicking is generated by several mechanisms in cells. Transposase catalyzes nicking at the ends of the inverted repeat (IR) in replicative transposition. Adaptation complexes nick leader-proximal repeat junctions of the CRISPR array during spacer integration. Rep protein nicks the double strand origin for DNA replication of a rolling circle replication (RCR) plasmid. R-loop formation induces nicking on the displaced strand and also can block replication fork progression leading to double-strand break. Nuclease / helicase can access DNA through the nicked or double-strand broken site and generate short DNA fragments. Cas1, Cas2 and Cas4 adaptation complex finds DNA fragment with an upstream CCN and downstream NW motif. The complex then processes the protospacer to 37 bp and integrates it as a new spacer into the CRISPR array.