Figure 5.
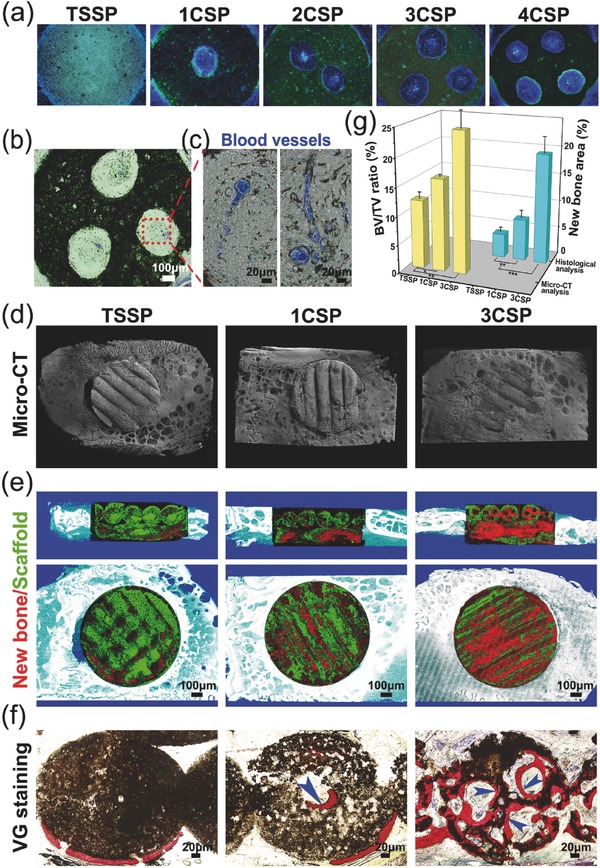
Characterizations of the lotus root‐like biomimetic scaffolds to enhance in vivo angiogenesis in rat muscle implantation and osteogenesis in rabbit calvarial defects. a) Fluorescence image of histological sections of biomimetic scaffolds stained with DAPI. b,c) The sections from microfil‐perfused samples were used to detect the new blood vessels, b) optical microscope image of 3CSP biomimetic scaffolds with blood vessels perfused by microfil, c) the magnified image of blood vessels (in blue) in the lotus root‐like structure. d) Typical 3D reconstruction micro‐CT images of the edges between materials and rabbit calvarial defects, and e) micro‐CT cross‐section images of rabbit calvarial defect regions (red for new bone tissues, green for materials). f) The undecalcified histological sections stained with Van Gieson's picrofuchsin, newly formed bone tissues (in red) can be well observed (blue arrows point to the new bone). g) Micro‐CT reconstruction analysis of the volume ratio of the newly formed bone to the defect regions (BV/TV) and histological morphometric analysis of the area of the newly formed bones in the whole defect regions at week 12. The 3CSP biomimetic materials showed significantly improvement in bone regeneration as compared to 1CSP and TSSP materials. (n = 6, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.)
