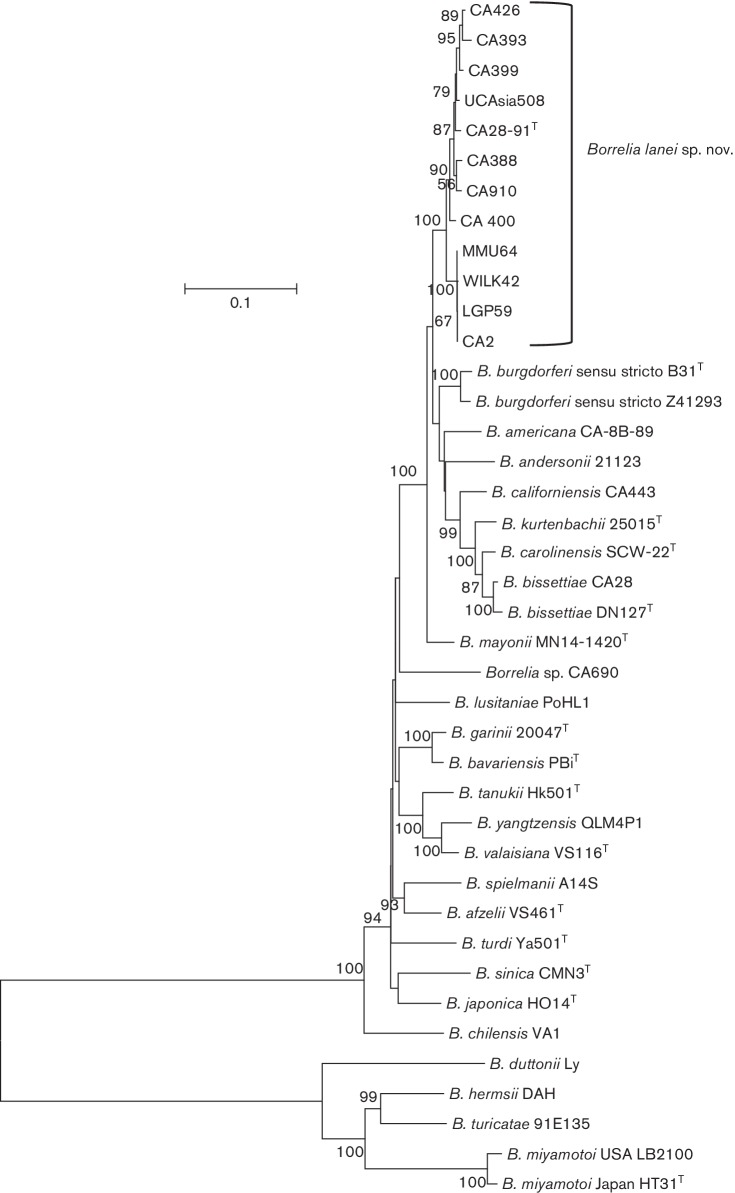
Fig. 1.
Molecular phylogenetic analysis of B. lanei sp. nov. The evolutionary history was inferred by using the maximum-likelihood method based on the general time reversible model [10]. The tree with the highest log likelihood (−33644, 4319) is shown. A discrete Gamma distribution was used to model evolutionary rate differences among sites [4 categories (+G, parameter=0, 6690)]. The rate variation model allowed for some sites to be evolutionarily invariable [(+I), 32, 8618 % sites]. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths measured in the number of substitutions per site (scale bar). B. lanei sp. nov. strains form a cluster containing two sister clades. Both sister clades form a separate cluster distinct from all other Borrelia genospecies known to date underlining this species is divergent.