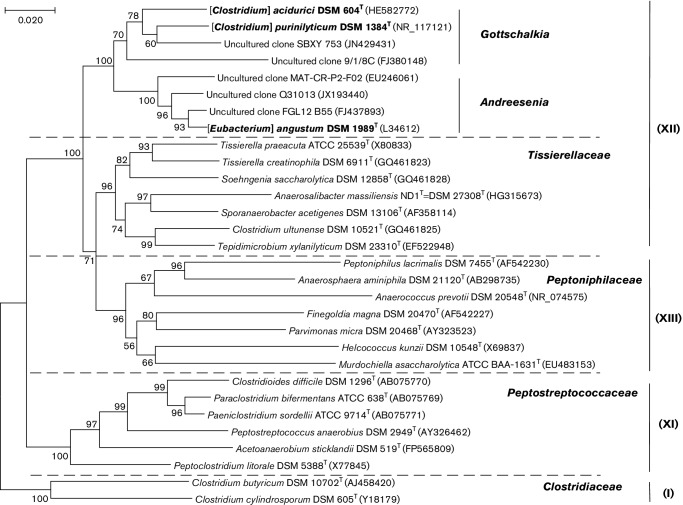
Fig. 1.
16S rRNA gene-based phylogenetic tree of Clostridium acidurici and related organisms and metagenomic samples. The names of the characterized members of the proposed genera Gottschalkia and Andreesenia are shown in bold in square brackets. The sequences from type strains (indicated with T) were used and listed under their DSM accession numbers; where available. GenBank accession numbers are listed in parentheses. Roman numerals on the right indicate the clostridial cluster assignments of Collins et al. [4]. Clostridioides difficile, Acetoanaerobium sticklandii and Peptoclostridium litorale are the recently assigned names of formerly misclassified Clostridium spp. [45, 46]. The tree was inferred using the neighborhood-joining method, based on the Tamura-Nei model [47] as implemented in mega7 [15]. The evolutionary distances were computed using the Jukes-Cantor method and are in the units of the number of base substitutions per site. The tree was rooted using sequences from C. butyricum and C. cylindrosporum, which are members of Clostridium sensu stricto (cluster I).