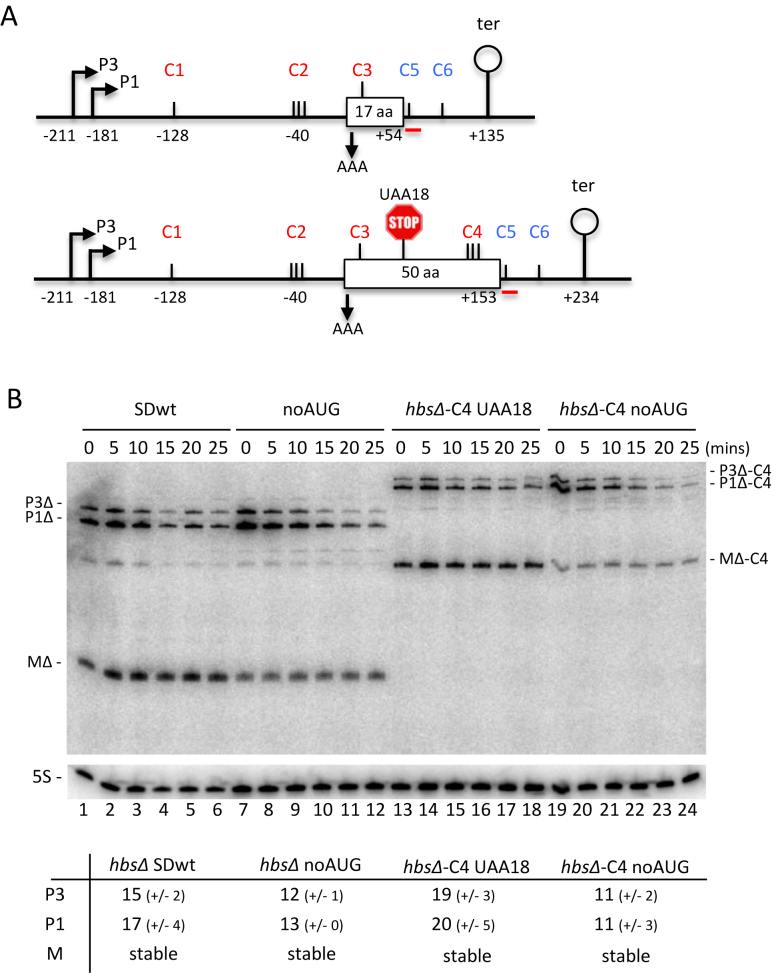
Figure 5.
Restoration of RNase Y cleavage site C4 within the hbs coding sequence does not destabilize the hbsΔ mRNA, even in the absence of ribosome traffic. (A) Schematics of the B. subtilis hbsΔ (above) and hbsΔ-C4 (below) mutant constructs. Labeling is as in Figure 1. Mutation of the AUG start codon to AAA in hbsΔ noAUG and hbsΔ-C4 noAUG is indicated with a downward pointing arrow. Mutation of the lysine codon 18 (AAA) to a stop codon (UAA) in hbsΔ-C4 UAA18 is indicated by a stop sign. (B) Northern blot of total RNA isolated from strains carrying the hbsΔ SDwt, and hbsΔ noAUG, hbsΔ-C4 noAUG and hbsΔ-C4 UAA18 mutant plasmids at different times after rifampicin addition (n = 2). The blot was probed with oligo CC429 (hbs), shown as a red line in panel A, and then HP246 (5S rRNA) as a loading control. Calculated half-lives of the major transcripts are given underneath the blot. Half-lives >30 min are referred to as stable. Average decay curves are shown in Supplementary Figure S1.