Figure 2.
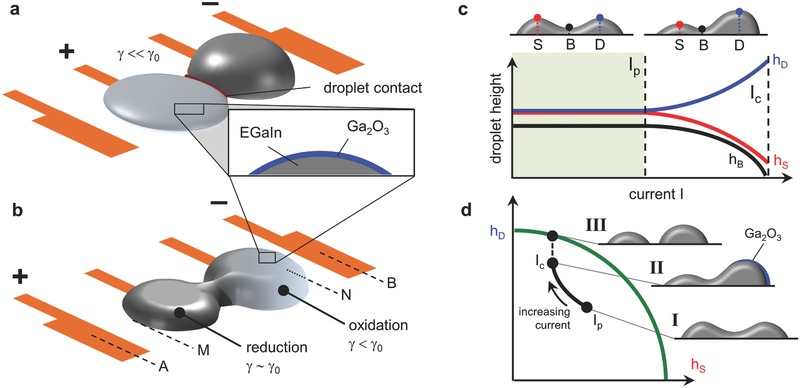
Summary of droplet coalescence and separation behavior. a) An oxidative potential is applied at the source electrode while the gate is negative. This causes spreading of the source EGaIn. Contact and coalescence occur between the source and drain. Positions A, B, M, and N are relevant for Equation (2). b) A positive voltage is applied at the counter relative to the gate. Oxidation occurs on the anodic pole of the EGaIn, and reduction occurs on the cathodic pole, causing a gradient of interfacial tension which eventually makes the system unstable. c) Droplet and bridge height as a function of current when voltage is applied across the counter and gate electrodes. Blue (h D) is the drain side, red (h S) is the source side, and black (h B) is the bridge. d) Heights of LM over the source and drain pads. The green curve follows the heights when drops are separated (limited by volume), and the black curve follows the heights when the drops are coalesced and as current is applied across the outer electrodes.
