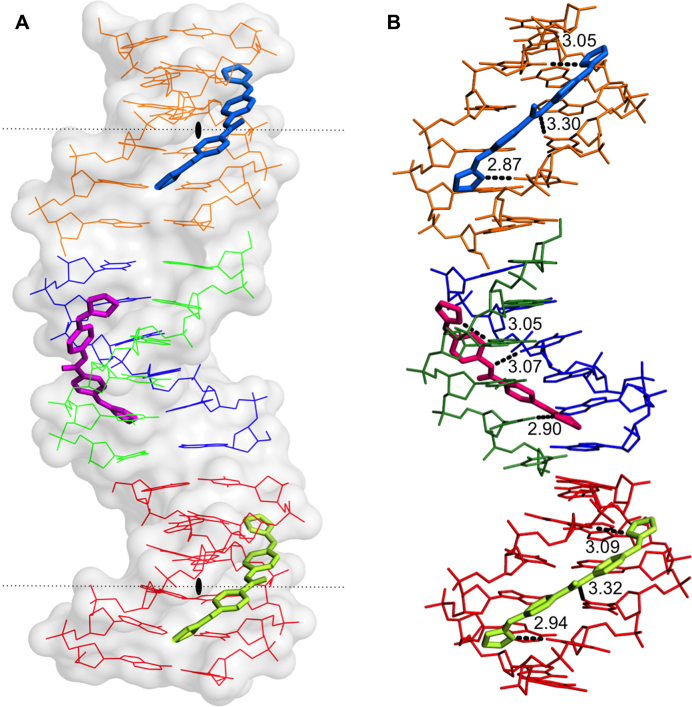
Figure 8.
(A) View of the different crystallographic units of the complex. The black lozenge indicates the dyad axes. There are four independent single oligonucleotides chains; two of them (blue-green) form the central duplex and the other two (orange and red) form two different DNA duplexes with their symmetrical chain. Three crystallographically independent drug molecules are indicated in different colours. Drug F (pink), Drugs E (green) and G (blue). (B) Hydrogen bonds formed by the drugs with the minor-groove atoms of the DNA duplexes show similar interactions. The orientation of the aromatic rings in the central drug (F, pink) differs from to the other two drugs. Drug E and G have two possible inverted positions in the groove; for clarity only one of them is shown.