Figure 4.
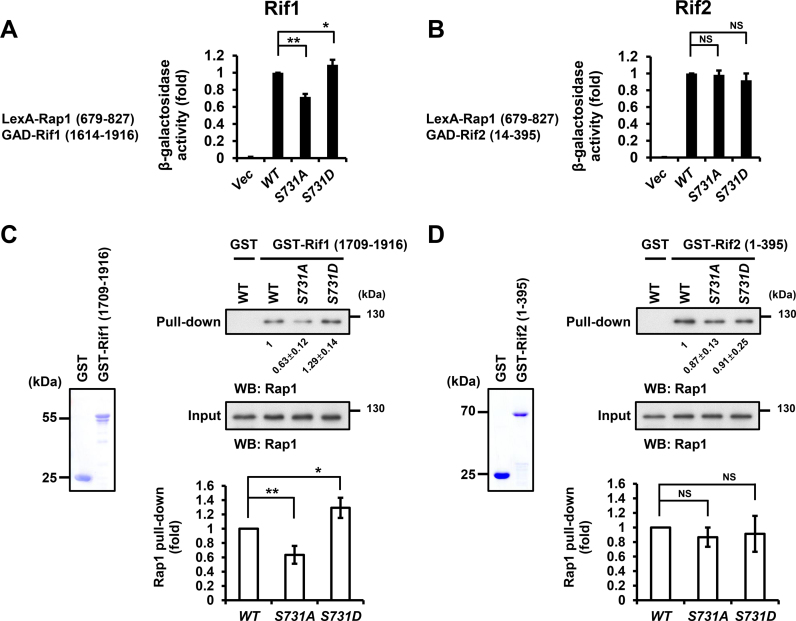
Rap1 S731A mutation reduces its interaction with Rif1, but not Rif2. (A) Yeast two-hybrid assay indicated that rap1-S731A mutation significantly reduces, whereas rap1-S731D increases, the Rap1–Rif1 interaction. The Y axis shows the relative folds of β-galactosidase activity. Error bars indicate the s.d. (n = 4, *P-values < 0.05, **P-values < 0.001, Student's t-test, two-tailed). (B) Yeast two-hybrid assay indicated that WT and rap1-S mutants display similar Rap1-Rif2 interaction (n = 4, NS, non-significant, Student's t-test, two-tailed,). Bars, s.d. (C) Left panel, the aliquot of GST and GST-Rif1 (1709–1916) fusion proteins was resolved on SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie blue. Top-right panel, GST pulldown assay indicated that GST-Rif1 (1709–1916) significantly reduce its interaction with Rap1-S731A, whereas increase that with Rap1-S731D. Lower panel, the quantitative data of GST-Rif1 pulldown (n = 4, *P-values < 0.05, **P-values < 0.001, Student's t-test, two-tailed). Bars, s.d. (D) Left panel, the aliquot of GST and GST-Rif2 (1–395) fusion proteins was resolved on SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie blue. Top-right panel, GST pulldown assay demonstrated that the level of GST-Rif2 (1–395) interacting with Rap1 is not significantly different between WT and Rap1-S731A or Rap1-S731D, respectively. Lower panel, the quantitative data of GST-Rif2 pulldown (n = 4, NS, non-significant, Student's t-test, two-tailed). Bars, s.d.