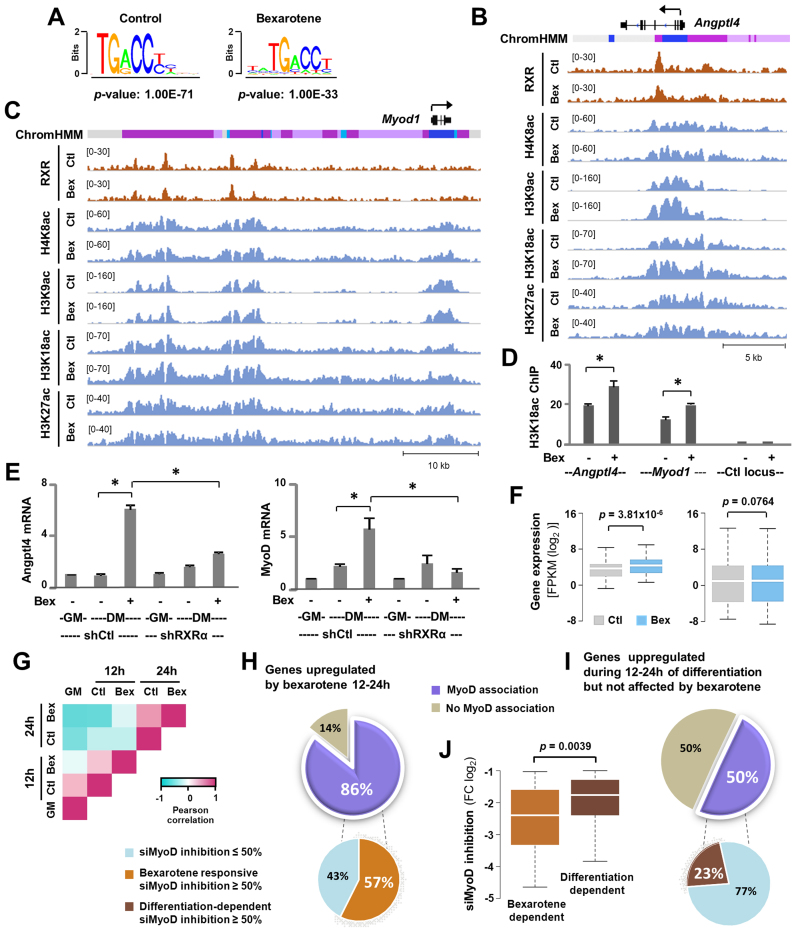
Figure 2.
RXR regulates MyoD expression. (A) Consensus binding sequences of nuclear receptors were discovered through de novo motif analysis of RXRα peaks in myoblasts differentiated for 24 h in the absence or presence of bexarotene (Ctl or Bex 50 nM). (B) Genome browser view of RXRα and histone acetylation signals at the Angptl4 locus. Black bars show Refseq gene position and ChromHMM track colors correspond to color designated to each chromatin state as in Figure 3A. (C) Genome browser view of the Myod1 locus. (D) H3K18ac enrichments at the Angptl4 and Myod1 locus were examined by qChIP analysis with an intergenic region as control. Enrichment was quantified as percentage of input (error bars: SEM; n = 3; *, P < 0.05). (E) RXRα-knockdown (shRXRα) myoblasts were differentiated with or without bexarotene for 24 h with proliferating myoblasts (GM) as controls. A non-silencing shRNA (shCtl) was used in parallel as control. The mRNA levels of Angptl4 and MyoD were assessed by RT-qPCR and plotted as fold change in relation to proliferating myoblasts (error bars: SEM; n = 3). (F) Expression levels of bexarotene responsive genes assigned to the RXRα peaks in differentiating myoblasts and that of all RXRα associated genes in differentiating myoblasts is presented as FPKM measured by RNA-seq. (G) The heatmap of Pearson correlation coefficients calculated between the row-based z-scores for bexarotene responsive genes. (H and I) MyoD association is categorized for the 147 genes upregulated by bexarotene between 12 and 24 h of differentiation and the 246 genes upregulated in the same period but not affected by bexarotene. A pie chart below displays the percentage of genes which exhibited a >50% of inhibition in C2C12 myoblasts differentiated for 24 h following siMyoD knockdown, compared to a non-specific silencing control. (J) Expression of MyoD-associated genes (the 86 and 50% group respectively) from the siMyoD knockdown microarrays is presented as fold change in relation to a non-specific silencing control.