Figure 4.
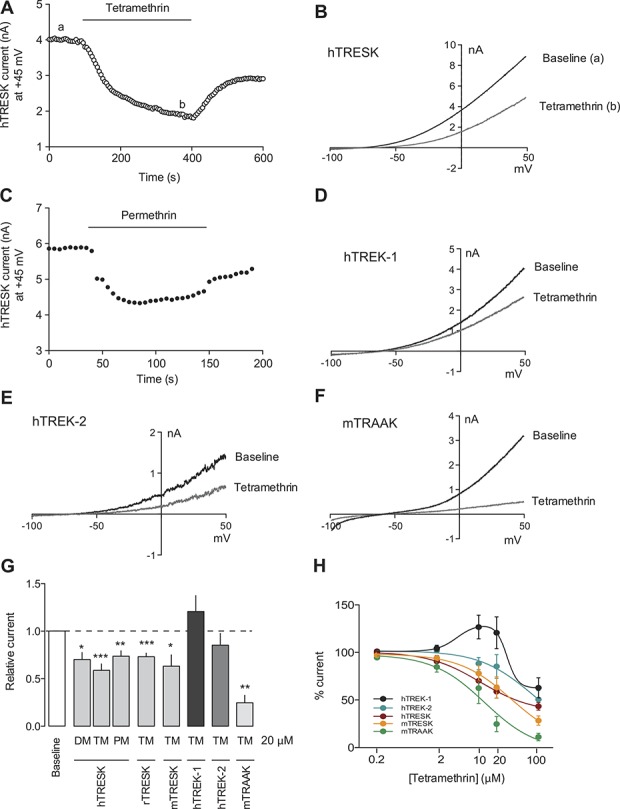
Pyrethroids inhibit K2P channels expressed in heterologous systems. (A) Whole-cell current in a HEK293 cell transfected with human TRESK. Depolarizing ramps from –100 to +50 mV every 5 seconds from a holding voltage of −60 mV were applied. Current measured at +45 mV in each ramp is plotted against time. Tetramethrin application (TM, 20 μM) produced a significant decrease in the current. Washout of the drug partially recovered current values. (B) Voltage ramps recorded in baseline (a) and during TM application (b) from the experiment shown in (A). (C) Permethrin (PM, 20 μM), a widely used drug as topical treatment for scabies and head lice, also inhibits hTRESK. TRESK current was recorded as in (A). (D–F) Effect of TM (100 μM) on human TREK-1 (D), human TREK-2 (20 μM, E), and mouse TRAAK (20 μM, F) expressed in HEK293 cells. (G) Quantification of inhibitory effects of pyrethroids in K2P channels. Currents were recorded as described for the experiment shown in (A). Tetramethrin, deltamethrin (DM), and PM were assayed at 20 μM. In each group, 6 to 10 cells were recorded per condition. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; and ***P < 0.001 Student t test vs baseline. (H) Dose–response relationships of hTRESK, mTRESK, hTREK-1, hTREK-2, and mTRAAK.
