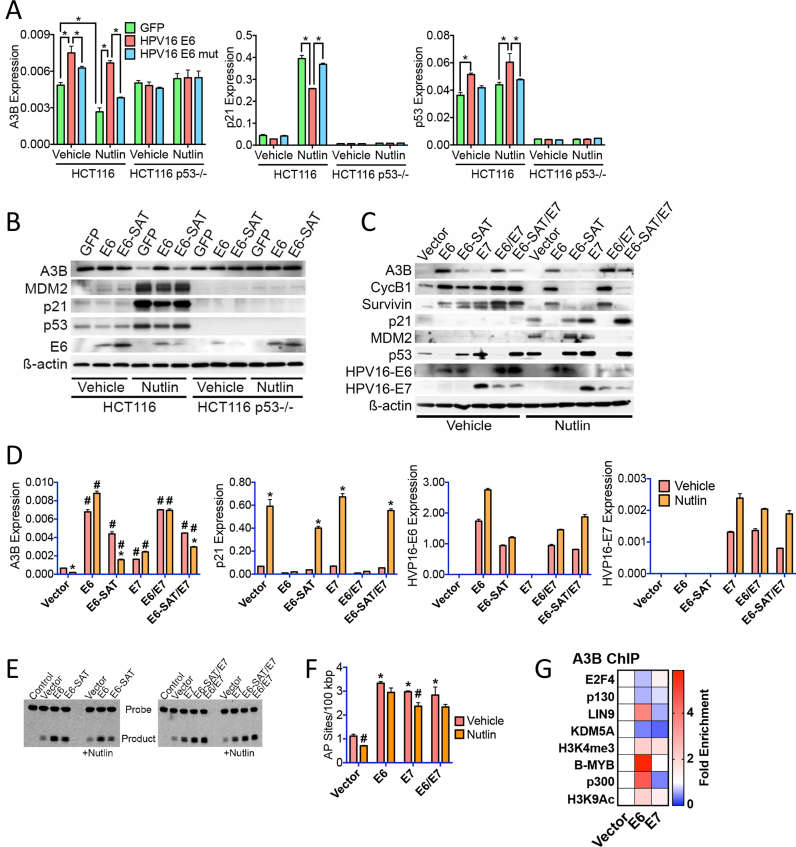
Figure 6.
HPV16 E6 and E7 viral oncogenes promote APOBEC3B expression and activity by inhibiting the action of the E2F4/p107/p130 DREAM transcriptional repression complex. (A) HCT116 and p53-null HCT116 cells were transfected with HPV16 E6 or the E6-SAT mutant that does not interact with p53. RT-qPCR was performed using RNA prepared 24 h following addition of Nutlin (10 μM). Asterisks show significant (P < 0.05; n = 3) differences in mRNA expression. (B) Cells treated as above, were processed for immunoblotting. (C) Normal immortalized human keratinocyte line (NIKS) stably transduced with E6, the E6-SAT mutant, E7, E6/E7, E7/mutant E6 or vector only, were treated with Nutlin (10 μM) for 24 h, followed by preparation protein lysates for immunoblotting. (D) NIKS were treated as in C, followed by preparation of total RNA and RT-qPCR. Asterisks show significant (P < 0.05) reduction in mRNA expression for Nutlin-treated samples relative to the vehicle treated NIKS for each transduced line. Cross-hatches show significant (P < 0.05) difference in mRNA expression relative to the vehicle treated and vector transduced NIKS. Results for three experiments are shown. (E) The in vitro cytidine deaminase assay was used to assess A3B activity in protein lysates prepared 24 h following addition of 10 μM Nutlin to the E6 and E7 transduced NIKS cells. (F) Quantification of biotin-labelled ARP conversion of abasic sites in genomic DNA from E6 and E7 transduced NIKS cells. Asterisks show significant (P < 0.05) differences in AP sites compared to vehicle-treated vector transduced NIKS; cross-hatches denote statistically significant reduction in AP sites by Nutlin treatment for each transduction. (G) ChIP-qPCR for vector, E6 or E7 transduced NIKS cells is shown as fold change in transcription factor/histone mark enrichment at the A3B gene promoter, relative to vehicle controls. The actual factor enrichment relative to input is shown in Supplementary Figure S7B.